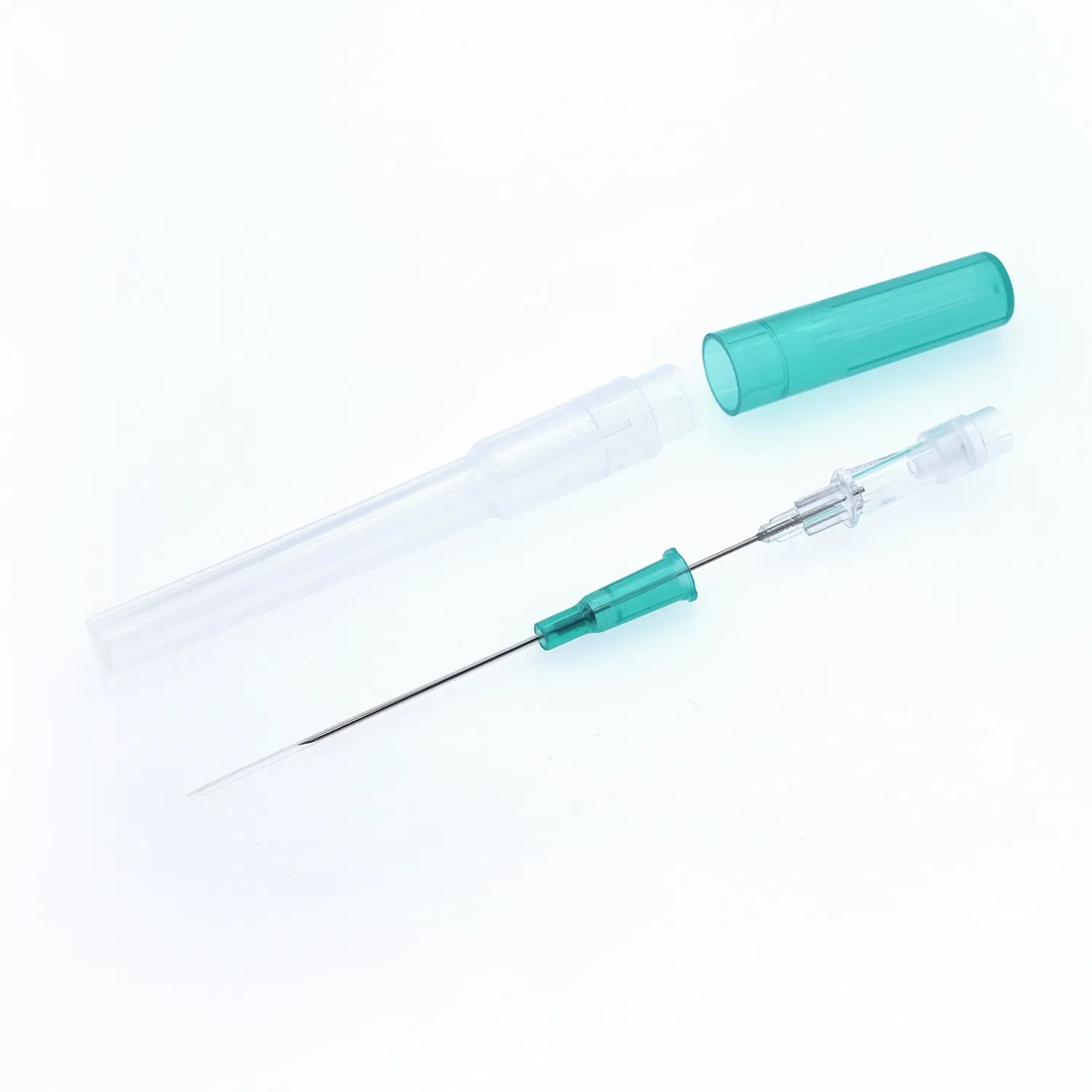
Intravenous cannulation stands as one of the most fundamental procedures in modern healthcare. Every day, millions of patients worldwide require vascular access for medication administration, fluid resuscitation, blood transfusions, and diagnostic procedures. The medical disposable IV cannula serves as the critical gateway for these therapies, making its proper selection and application essential for positive patient outcomes.
This comprehensive guide explores the practical applications, clinical benefits, and technical considerations of medical disposable IV cannulas, particularly focusing on pen-type designs ranging from 14G to 26G gauges.
What is an IV Cannula?
An intravenous cannula is a thin, flexible tube inserted into a patient’s vein to provide direct access to the circulatory system. Unlike traditional needles that remain in the vein, an IV cannula consists of two components:
- The introducer needle – A sharp, beveled needle that punctures the skin and vein
- The catheter – A flexible tube that remains in the vein after the needle is withdrawn
This design allows the catheter to stay in place for extended periods (typically 72-96 hours) while minimizing the risk of vessel perforation and patient discomfort.
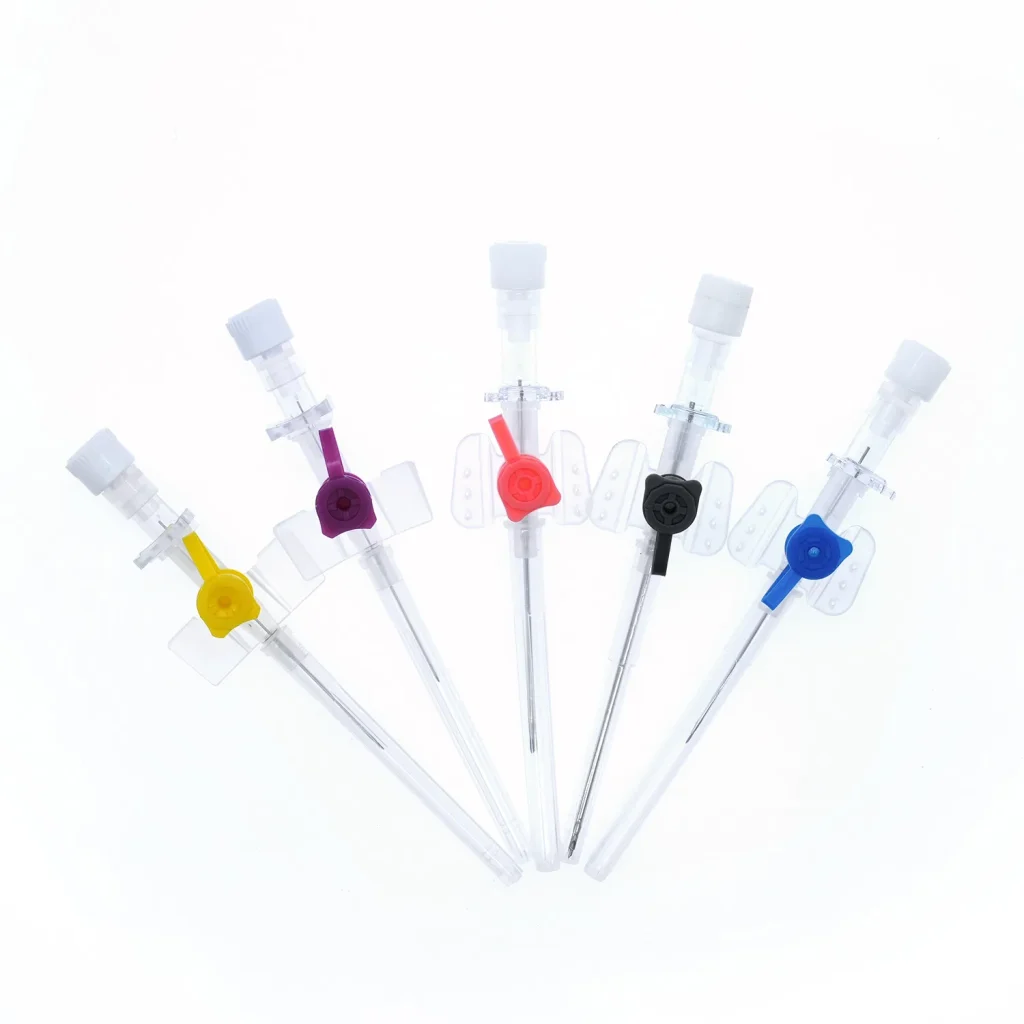
Primary Clinical Applications
Emergency Medicine and Trauma Care
In emergency departments and trauma scenarios, rapid vascular access can be life-saving. Large-bore IV cannulas (14G-16G) enable:
- Rapid fluid resuscitation for shock patients
- Emergency blood transfusions at high flow rates
- Immediate medication delivery in cardiac arrest situations
- Contrast media administration for emergency CT scans
The 3-facet needle point design reduces penetration force, allowing healthcare providers to establish access quickly even under high-pressure conditions.
Surgical Procedures
Operating rooms require reliable venous access throughout procedures. IV cannulas serve multiple purposes:
- Anesthesia administration for induction and maintenance
- Intraoperative fluid management to maintain hemodynamic stability
- Blood product transfusion during surgeries with anticipated blood loss
- Medication delivery including antibiotics, analgesics, and paralytic agents
Medium-gauge cannulas (18G-20G) provide optimal balance between flow rate and vessel preservation for most surgical patients.
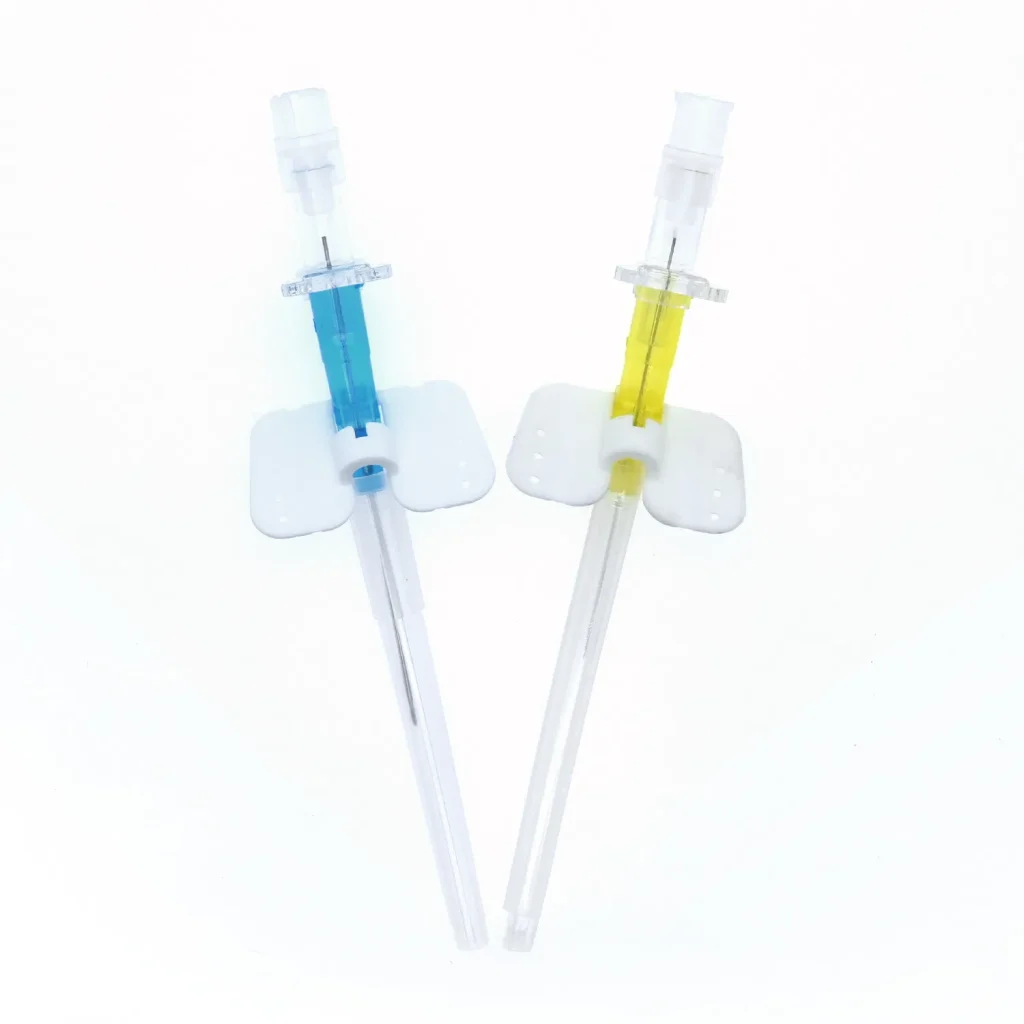
General Medical Wards
In non-critical care settings, IV cannulas facilitate routine therapeutic interventions:
- Antibiotic therapy for infections requiring intravenous administration
- Hydration support for patients unable to maintain oral intake
- Electrolyte replacement for imbalances
- Chemotherapy infusions in oncology units
- Pain management through continuous or intermittent analgesic delivery
Standard gauges (20G-22G) meet most general ward requirements while minimizing patient discomfort.
Pediatric and Neonatal Care
Smaller patients require specialized cannulation approaches. Fine-gauge IV cannulas (24G-26G) are specifically designed for:
- Neonatal intensive care where vessels are extremely small
- Pediatric medication administration with appropriate flow rates
- Infant hydration therapy during illnesses
- Vaccination and immune therapy requiring IV access
The thin-wall construction maintains adequate flow rates even in smaller gauge sizes, crucial for pediatric dosing accuracy.
Geriatric Medicine
Elderly patients often present with fragile, difficult-to-access veins. Appropriate IV cannula selection addresses these challenges:
- Smaller gauge options (22G-24G) reduce vessel trauma
- Kink-resistant catheters prevent occlusion in mobile patients
- Transparent flashback chambers aid visualization in patients with poor venous return
- Secure fixation wings minimize dislodgement risk
Key Functional Features and Clinical Benefits
3-Facet Needle Point Technology
The precisely ground 3-facet bevel serves specific clinical purposes:
- Reduced insertion force means less pain for patients and easier venipuncture for practitioners
- Clean vessel entry minimizes endothelial damage and reduces phlebitis risk
- Higher first-attempt success rates decrease patient anxiety and procedure time
- Preserved vein integrity allows for future cannulation attempts if needed
Transparent Flashback Chamber
This seemingly simple feature provides critical clinical information:
- Immediate confirmation of successful vein entry through blood visualization
- Reduces blind advancing that can cause vessel perforation
- Enhances confidence for less experienced practitioners
- Decreases procedure time by eliminating guesswork
Kink-Resistant Catheter Material
Modern PTFE, FEP, and PU materials offer distinct advantages:
- Maintains patency during patient movement and position changes
- Prevents flow obstruction that could delay medication delivery
- Extends dwell time by reducing mechanical complications
- Improves patient comfort through flexible material that moves with tissue
Thin-Wall Construction
This engineering innovation directly impacts clinical performance:
- Maximizes internal diameter without increasing external gauge size
- Increases flow rates by up to 30% compared to standard-wall catheters
- Enables rapid infusions critical in emergency situations
- Reduces infusion time for routine medication administration
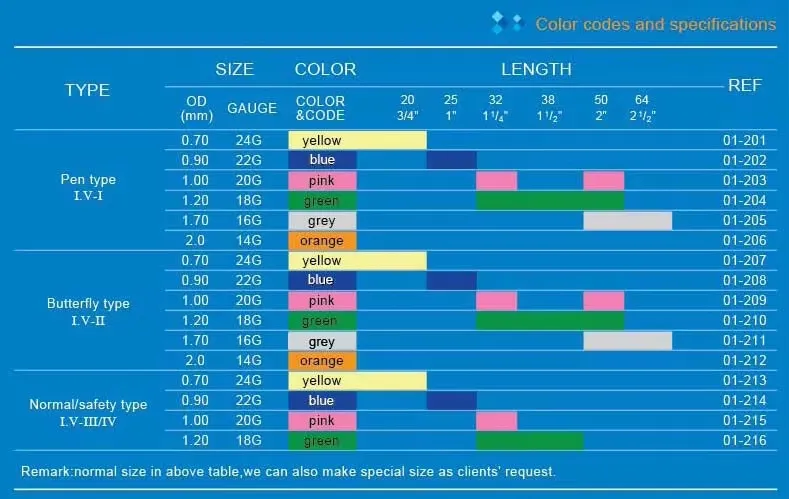
Color-Coded System
International standardization provides universal benefits:
- Eliminates gauge confusion across different manufacturers and countries
- Speeds emergency procedures through instant visual identification
- Reduces medication errors by ensuring appropriate gauge for prescribed infusions
- Facilitates training with consistent global standards
Luer Lock Connection
This standardized fitting system ensures:
- Leak-proof connections preventing medication waste and contamination
- Universal compatibility with all standard IV administration sets
- Secure attachment that withstands patient movement
- Quick disconnect capability for emergency situations
Injection Port Integration
The built-in injection port serves multiple functions:
- Medication administration without disconnecting primary infusions
- Blood sampling through the cannula, reducing additional needlesticks
- Emergency drug delivery during resuscitation
- Flush administration to maintain catheter patency
Gauge Selection: Matching Clinical Need to Cannula Size
14G-16G: High-Flow Applications
Primary Uses:
- Trauma resuscitation requiring massive transfusion protocols
- Major surgical procedures with anticipated significant blood loss
- Rapid contrast administration for imaging studies
- Emergency fluid resuscitation in severe dehydration or shock
Flow Rate Advantage: These large-bore cannulas can deliver fluids at rates exceeding 300 mL/minute, essential when every second counts.
Consideration: Reserve for patients with adequate vein size and critical clinical need due to increased insertion trauma.
18G-20G: Standard Adult Care
Primary Uses:
- Elective surgical procedures
- Blood transfusions
- General intravenous therapy
- Medication administration requiring moderate flow rates
Flow Rate Advantage: Provides 80-200 mL/minute flow rates, sufficient for most clinical scenarios while being easier to insert than larger gauges.
Consideration: The optimal choice for most adult patients, balancing efficacy with patient comfort.
22G-24G: Specialized and Pediatric Applications
Primary Uses:
- Pediatric patients with smaller vessels
- Elderly patients with fragile veins
- Hand or foot cannulation where vessels are naturally smaller
- Long-term therapy where vein preservation is prioritized
Flow Rate Advantage: Delivers 35-60 mL/minute, adequate for most medications and maintenance fluids.
Consideration: Ideal when vein preservation and patient comfort outweigh need for rapid infusion.
26G: Neonatal and Specialized Use
Primary Uses:
- Neonatal intensive care
- Premature infant therapy
- Scalp vein cannulation in infants
- Extremely fragile adult veins as last resort
Flow Rate Advantage: Provides controlled flow of 20-30 mL/minute, appropriate for small patient volumes.
Consideration: Requires specialized training due to technical difficulty and small margin for error.
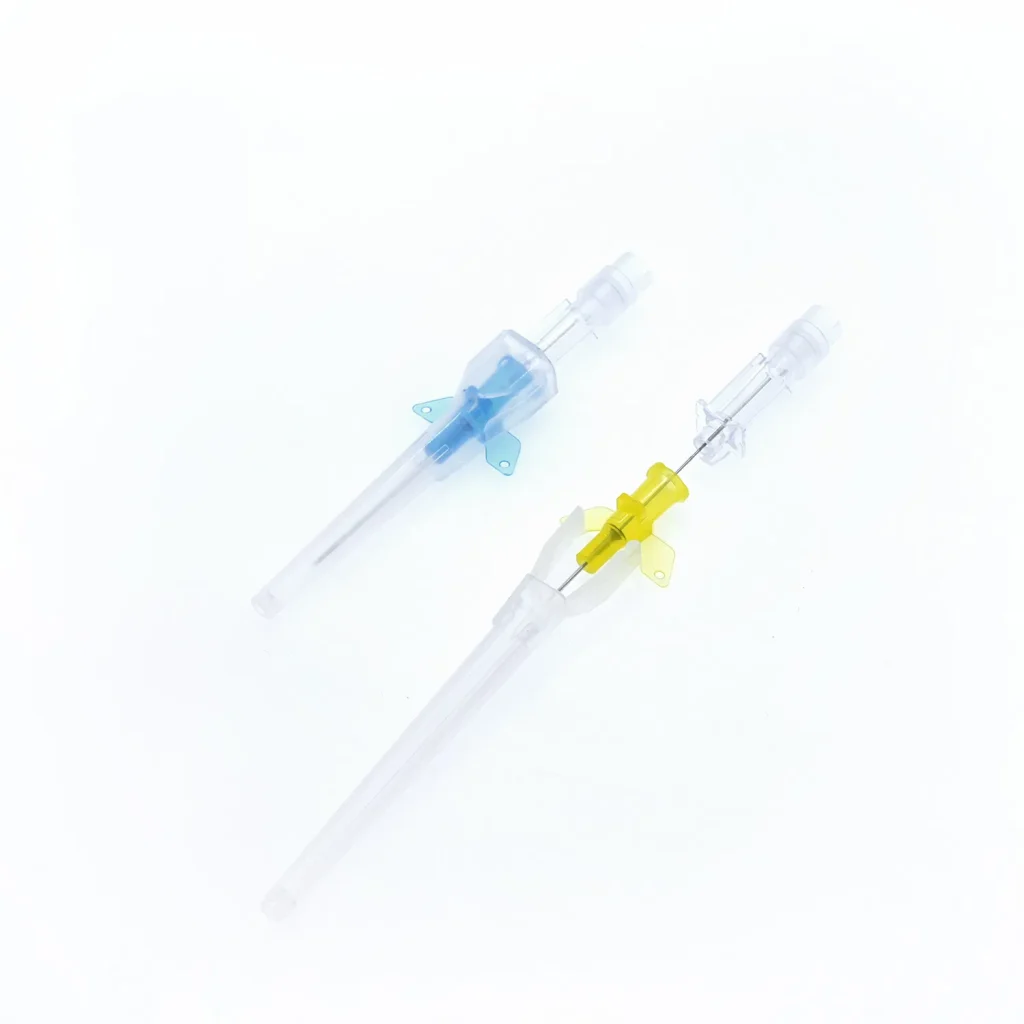
Pen-Type Design: Ergonomic Advantages in Clinical Practice
The pen-type IV cannula configuration offers distinct handling benefits:
Enhanced Grip Control
The pen-like grip allows practitioners to:
- Hold the device like a writing instrument, utilizing familiar motor patterns
- Maintain steady control during insertion through natural hand positioning
- Apply precise directional force for accurate vein entry
- Reduce hand fatigue during multiple cannulation attempts
Improved Insertion Angle Management
The design facilitates:
- Consistent 15-30 degree insertion angles optimal for venipuncture
- Better tactile feedback during vessel entry
- Easier catheter advancement after successful puncture
- Reduced risk of through-and-through vessel perforation
Single-Handed Operation Capability
In emergency situations, pen-type cannulas enable:
- One-hand insertion while stabilizing the patient with the other hand
- Faster procedure completion in critical patients
- Better control in moving vehicles (ambulances, helicopters)
- Reduced need for additional personnel assistance
Safety Features and Infection Prevention
Hydrophobic Filter Integration
This component provides critical protection:
- Prevents blood backflow into the flashback chamber during patient movement
- Reduces contamination risk for healthcare workers during handling
- Maintains sterility of the catheter hub
- Allows air venting while blocking fluid passage
Sterile Soft Blister Packaging
The packaging design ensures:
- Sterility maintenance until point of use
- Easy opening for rapid deployment in emergencies
- Visual integrity confirmation through transparent materials
- Protection during transport and storage
Single-Use Disposable Design
This fundamental feature prevents:
- Cross-contamination between patients
- Bloodborne pathogen transmission
- Healthcare-associated infections
- Dulled needle complications from reuse attempts

Clinical Best Practices for IV Cannula Use
Site Selection
Optimal vein selection improves success rates:
- Forearm veins (cephalic, basilic) for routine therapy
- Antecubital fossa for emergency access, though limits arm mobility
- Hand veins when forearm access unavailable, using smaller gauges
- Avoid lower extremities in adults due to thrombosis risk
Insertion Technique
Proper technique ensures patient safety:
- Apply tourniquet 10-15 cm above intended site
- Cleanse site with appropriate antiseptic (chlorhexidine preferred)
- Stabilize vein with non-dominant hand
- Insert at 15-30 degree angle with bevel up
- Watch for flashback confirming vein entry
- Lower angle and advance catheter while withdrawing needle
- Release tourniquet before flushing
- Secure with appropriate dressing
Maintenance and Monitoring
Post-insertion care prevents complications:
- Assess site every 4-8 hours for signs of infiltration or phlebitis
- Flush regularly (every 8-12 hours minimum) to maintain patency
- Replace dressings when soiled or per facility protocol (typically every 5-7 days)
- Remove promptly when no longer clinically necessary (within 72-96 hours typically)
Common Complications and Prevention Strategies
Phlebitis (Vein Inflammation)
Prevention:
- Select appropriate gauge for vein size
- Use proper aseptic technique during insertion
- Rotate sites every 72-96 hours
- Flush adequately to prevent chemical irritation
- Avoid vesicant medications in small veins
Infiltration and Extravasation
Prevention:
- Secure cannula properly to prevent movement
- Assess site before each medication administration
- Educate patients to report pain, swelling, or coolness
- Use infusion pumps with pressure alarms
- Choose stable vein locations avoiding joints
Occlusion
Prevention:
- Use kink-resistant catheters (as in these pen-type designs)
- Flush with adequate pressure (10 mL syringe minimum)
- Avoid blood sampling when possible
- Position cannula away from joint flexion points
- Implement flushing protocols consistently
Infection
Prevention:
- Maintain strict aseptic technique during insertion
- Use chlorhexidine skin preparation
- Apply sterile transparent dressings
- Minimize hub access and use needleless systems
- Remove cannulas promptly when no longer needed

Quality Specifications and Regulatory Compliance
Material Standards
Modern IV cannulas must meet rigorous requirements:
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene):
- Biocompatible with minimal tissue reaction
- Smooth surface reduces thrombus formation
- Chemically inert with wide medication compatibility
- Radiopaque options available for imaging verification
FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene):
- Similar properties to PTFE with improved clarity
- Enhanced visualization of catheter in vein
- Excellent kink resistance
- Lower friction coefficient for easier insertion
PU (Polyurethane):
- Softens at body temperature for increased comfort
- Superior kink resistance
- Thinner walls possible for given outer diameter
- Excellent long-term biocompatibility
Manufacturing Standards
Quality IV cannulas adhere to:
- ISO 10555 standards for intravascular catheters
- ISO 13485 certification for medical device manufacturing quality management
- Sterility assurance level (SAL) of 10⁻⁶ for ethylene oxide sterilization
- Biocompatibility testing per ISO 10993 series
- Latex-free construction to prevent allergic reactions

Cost-Effectiveness in Healthcare Settings
Direct Cost Considerations
Quality IV cannulas provide measurable economic benefits:
Reduced Procedure Time:
- Higher first-attempt success rates decrease staff time per insertion
- Clear flashback chambers eliminate guesswork
- Ergonomic design reduces practitioner fatigue
Fewer Complications:
- Kink-resistant materials reduce replacement frequency
- Proper gauge selection prevents phlebitis-related early removal
- Quality materials extend safe dwell time
Decreased Supply Waste:
- Successful first attempts use fewer cannulas per patient
- Extended patency reduces replacement frequency
- Reliable performance minimizes emergency replacements
Indirect Cost Benefits
Patient Satisfaction:
- Less painful insertions improve patient experience scores
- Fewer reinsertions reduce anxiety and discomfort
- Successful therapy delivery supports positive outcomes
Staff Efficiency:
- Standardized color coding reduces training time
- Reliable performance builds practitioner confidence
- Fewer complications free staff for other patient care
Risk Management:
- Quality devices reduce complication-related liability
- Consistent performance supports better documentation
- Regulatory compliance prevents costly violations
Procurement Considerations for Healthcare Facilities
Volume Requirements Assessment
Facilities should calculate needs based on:
- Patient volume and typical length of stay
- Procedure types requiring specific gauge distributions
- Par levels needed for emergency preparedness
- Expiration management to minimize waste
Gauge Distribution Strategy
Typical hospital inventory includes:
- 30-40% in 20G for general adult use
- 25-30% in 18G for surgical and emergency applications
- 20-25% in 22G for pediatric and geriatric patients
- 10-15% in 14G-16G for trauma and critical care
- 5-10% in 24G-26G for specialized applications
Quality vs. Price Analysis
Evaluating true value requires considering:
- First-stick success rates impact overall costs
- Complication rates affect patient outcomes and readmissions
- Dwell time influences replacement frequency
- Staff satisfaction impacts efficiency and morale
Future Developments in IV Cannula Technology
Emerging Innovations
Current research focuses on:
- Integrated safety mechanisms to prevent needlestick injuries automatically
- Antimicrobial coatings to reduce infection rates
- Smart cannulas with embedded sensors monitoring patency and positioning
- Ultrasound-guided features built into the device
- Biodegradable components for environmental sustainability
Clinical Impact Potential
These advancements promise:
- Further reduction in healthcare-associated infections
- Improved success rates in difficult-access patients
- Real-time monitoring preventing complications
- Enhanced safety for healthcare workers
- Reduced environmental impact of medical waste
Conclusion
The medical disposable IV cannula represents a critical intersection of engineering precision and clinical necessity. From emergency trauma resuscitation to routine medication administration, these devices enable modern healthcare delivery across every specialty and patient population.
Understanding the specific features—3-facet needle points, transparent flashback chambers, kink-resistant materials, thin-wall construction, and standardized color coding—empowers healthcare professionals to select appropriate devices for each clinical situation. The pen-type design enhances ergonomics and control, while quality materials ensure safety and efficacy throughout the therapy duration.
For healthcare facilities, procurement decisions should balance initial costs against clinical performance, complication rates, and overall value. Quality IV cannulas with proven design features ultimately reduce costs through improved success rates, extended dwell times, and fewer complications.
As technology continues advancing, IV cannulation will become even safer, more effective, and more patient-friendly. However, the fundamental principles—proper gauge selection, aseptic technique, appropriate maintenance, and timely removal—remain the foundation of successful intravenous therapy.
Whether establishing access in a critically ill trauma patient or providing routine antibiotic therapy in a general ward, the medical disposable IV cannula stands as an indispensable tool in the modern healthcare provider’s arsenal.

About the Author: This guide was developed through analysis of clinical best practices, manufacturer specifications, and evidence-based medical literature to provide practical information for healthcare professionals and procurement decision-makers.