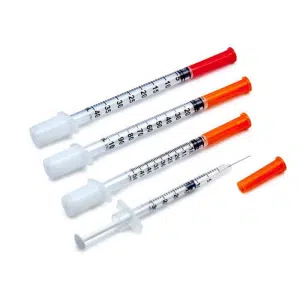
As the global veterinary healthcare market continues to expand, pet cat syringes have become essential medical supplies for home care. As a professional medical syringe manufacturer, we understand that selecting the right syringe for your feline companion is crucial for their health and wellbeing. This comprehensive guide, written from the perspective of an experienced syringe factory, will provide detailed insights into syringe selection criteria, application scenarios, and safe usage protocols for cat owners and veterinary professionals.
Understanding Pet Cat Syringe Applications: A Manufacturing Perspective
In modern veterinary medicine, the demand for veterinary syringes has increased significantly. Professional syringe manufacturing companies have developed specialized product lines tailored to feline physiological characteristics and clinical requirements.
1. Vaccination Syringes for Feline Immunization
Kittens require their first vaccination series starting at approximately 8 weeks of age, including FVRCP (feline viral rhinotracheitis, calicivirus, and panleukopenia) and rabies vaccines. Sterile disposable syringes in 1ml specifications are the industry standard for vaccine administration. Leading syringe manufacturers produce these precision instruments with graduation marks accurate to 0.01ml, ensuring precise dosage delivery critical for vaccine efficacy.
Key manufacturing specifications for vaccine syringes:
- Capacity: 0.5ml – 1ml (insulin-type preferred)
- Needle gauge: 25G – 27G (0.5mm – 0.4mm diameter)
- Barrel material: Medical-grade polypropylene (PP) with high transparency
- Sterilization method: Ethylene oxide (EO) or gamma radiation
- Quality standard: ISO 7886-1 compliance
2. Therapeutic Injection Syringes for Medication Administration
Pharmaceutical-grade syringes used for subcutaneous or intramuscular drug delivery require exceptional precision. Professional syringe production facilities manufacture specialized insulin syringes (0.3ml – 1ml) with ultra-fine graduations for medications requiring exact dosing, such as:
- Insulin for diabetic cats
- Antibiotics (enrofloxacin, amoxicillin-clavulanate)
- Pain management medications (buprenorphine, meloxicam)
- Immunosuppressants for chronic conditions
- Hormone therapies
Quality benchmarks from leading syringe factories:
- Graduation accuracy: ±5% tolerance
- Dead space minimization: <0.07ml residual volume
- Plunger smoothness: Siliconized for effortless operation
- Luer lock compatibility: Standard or slip-tip options
- Latex-free components: Preventing allergic reactions
3. Subcutaneous Fluid Administration Syringes
For geriatric cats or those with chronic kidney disease (CKD), regular subcutaneous fluid therapy is often necessary. Large-capacity syringes (10ml – 60ml) manufactured by specialized medical syringe factories are designed specifically for fluid administration. These bulk veterinary syringes are engineered with:
- High-flow barrel design for rapid fluid delivery
- Reinforced plunger seals preventing leakage under pressure
- Clear, bold graduation markings for accurate volume measurement
- Compatible Luer connections for IV extension sets and butterfly needles
- Durable construction suitable for controlled fluid therapy protocols
Technical specifications for fluid therapy syringes:
- Capacity range: 10ml, 20ml, 30ml, 50ml, 60ml
- Recommended needle gauge: 18G – 21G (for fluid flow optimization)
- Barrel transparency: Crystal-clear medical-grade polymer
- Pressure resistance: Tested to 50 psi without deformation
- Packaging: Individual sterile peel-packs with expiration dating
4. Needle-Free Oral Medication Syringes
Post-surgical care and nutritional supplementation often require oral feeding syringes. These specialized pet care syringes manufactured with food-grade materials feature:
- Needle-free safety design eliminating puncture risks
- Soft, flexible tips for gentle oral administration
- Graduated markings for precise liquid medication or nutrition delivery
- Easy-grip barrel design for single-handed operation
- Reusable construction with autoclavable materials (where specified)
Manufacturing standards for oral syringes:
- Material: FDA-approved food-grade polypropylene or polyethylene
- Tip design: Rounded, soft-touch for oral comfort
- Capacity options: 1ml, 3ml, 5ml, 10ml, 20ml
- Chemical resistance: Compatible with oils, suspensions, and aqueous solutions
- Cleaning protocol: Dishwasher-safe or sterilization-compatible
Global Pet Cat Market Analysis and Syringe Demand Trends
Understanding the global distribution of pet cats provides crucial context for veterinary syringe suppliers and medical device manufacturers targeting this growing market segment.
North American Market: The Largest Pet Cat Population
United States Market Dynamics
According to the American Pet Products Association (APPA) 2024 statistical report, approximately 46.8 million households in the United States own cats, representing over 30% of all pet-owning families. This translates to an estimated 82-95 million pet cats nationwide, making the U.S. the world’s largest single market for feline medical syringes.
Market drivers for syringe manufacturers:
- Increasing prevalence of chronic feline diseases (diabetes, CKD, hyperthyroidism)
- Growing trend of at-home veterinary care and telemedicine
- Rising pet healthcare expenditure ($136.8 billion in 2024)
- Expansion of veterinary compounding pharmacies requiring precision syringes
- Regulatory support through FDA veterinary device pathways
Canadian Market Insights
Canada hosts approximately 8.9 million pet cats, surpassing the canine population. The Canadian Veterinary Medical Association (CVMA) reports steady growth in preventive care and chronic disease management, driving demand for high-quality veterinary syringes from certified medical syringe manufacturers.
Key market characteristics:
- Higher per-pet healthcare spending compared to U.S. ($1,720 CAD annually)
- Strong preference for premium, safety-engineered syringe products
- Bilingual packaging requirements (English/French)
- Health Canada medical device licensing requirements
- Growing export market to U.S. via cross-border veterinary supply chains
European Market: Diverse Regulations and High Quality Standards
Continental Europe Pet Cat Statistics
The European Pet Food Industry Federation (FEDIAF) 2023 comprehensive survey documented approximately 126 million pet cats across Europe, distributed as follows:
Major European Cat Populations:
- Germany: 15.8 million cats (Europe’s largest market)
- France: 14.7 million cats (strong veterinary infrastructure)
- United Kingdom: 11.8 million cats (post-Brexit regulatory independence)
- Italy: 9.8 million cats (growing adoption rates)
- Poland: 6.8 million cats (emerging market potential)
- Netherlands: 6.2 million cats (high veterinary care standards)
- Spain: 6.0 million cats (Mediterranean lifestyle integration)
- Belgium: 2.2 million cats (dense urban pet ownership)
European Union Medical Device Regulations (MDR) Impact
All syringe manufacturing companies supplying the European market must comply with stringent MDR requirements effective since May 2021. This regulatory framework demands:
- CE marking certification through Notified Body assessment
- Comprehensive technical documentation and clinical evaluation
- Post-market surveillance and vigilance reporting systems
- Unique Device Identification (UDI) traceability
- Biocompatibility testing per ISO 10993 standards
Implications for syringe factories: Quality-focused European syringe manufacturers have established rigorous production protocols exceeding basic ISO 13485 requirements. These facilities invest heavily in:
- Cleanroom manufacturing environments (ISO Class 7 or 8)
- Automated inspection systems with 100% visual verification
- Validated sterilization processes with biological indicators
- Materials sourcing from EU-approved suppliers only
- Comprehensive batch documentation and release testing
Market opportunities:
- Premium product positioning based on superior quality standards
- Export potential to Middle East, Africa, and Asian markets
- Private label manufacturing for veterinary pharmacy chains
- Specialty syringe designs for exotic and large cat breeds
- Sustainable packaging initiatives meeting EU Green Deal objectives
Can Cats Use Human-Sized Syringes? Expert Analysis from Syringe Manufacturers
This frequently asked question deserves a comprehensive technical answer from the medical syringe production perspective.
The Short Answer: Yes, With Important Considerations
Professional syringe manufacturers produce veterinary and human medical syringes using identical base specifications per ISO 7886 standards. However, optimal feline applications require careful selection of capacity, needle gauge, and design features.
Detailed Capacity Selection Guide
Clinical Application Matrix:
Vaccination and Immunization:
- Recommended capacity: 0.5ml – 1ml (insulin syringe type)
- Needle specification: 27G – 29G × 1/2″ (0.4mm – 0.33mm × 12.7mm)
- Graduation precision: 0.01ml increments
- Dead space: <0.05ml to minimize vaccine waste
- Typical vaccines: FVRCP, FeLV, rabies (0.25ml – 1ml doses)
- Manufacturing consideration: Ultra-fine needles require specialized grinding and coating processes
Routine Medication Injection:
- Recommended capacity: 1ml – 3ml standard syringes
- Needle specification: 23G – 25G × 5/8″ to 1″ (0.6mm – 0.5mm × 16-25mm)
- Application examples: Antibiotics (0.5-2ml), pain medications (0.1-0.5ml)
- Plunger design: Smooth-glide silicone coating for controlled injection
- Luer connection: Standard slip-tip or Luer-lock for secure needle attachment
- Manufacturing consideration: Balanced plunger resistance prevents over-rapid injection
Subcutaneous Fluid Therapy:
- Recommended capacity: 10ml – 20ml (occasionally 35ml – 60ml)
- Needle specification: 18G – 21G × 1″ to 1.5″ (1.2mm – 0.8mm × 25-38mm)
- Typical volume per site: 50-150ml total (administered via multiple syringe fills or fluid bag)
- Barrel design: Wide-diameter for high-volume, low-pressure delivery
- Tip compatibility: Must accommodate standard IV extension sets
- Manufacturing consideration: Reinforced barrel walls prevent warping under sustained pressure
Oral Medication and Nutrition:
- Recommended capacity: 5ml – 10ml (needle-free design)
- Tip design: Soft, rounded oral adapter (15-20mm length)
- Material: Food-grade PP or silicone tip material
- Applications: Liquid medications, nutritional supplements, water supplementation
- Reusability: Some models designed for cleaning and repeated use
- Manufacturing consideration: Tip flexibility engineered to prevent oral injury while maintaining structural integrity
Needle Gauge Selection: Critical Considerations for Feline Anatomy
Anatomical factors affecting needle choice:
Cats possess unique dermal and muscular characteristics requiring specialized needle selection:
Skin structure:
- Feline epidermis: 30-40% thinner than canine or human skin
- Subcutaneous mobility: Highly elastic “scruff” tissue ideal for injection
- Pain receptor density: Higher concentration requiring ultra-sharp needles
- Hair follicle penetration: Fine needles reduce follicle trauma and post-injection bleeding
Muscle mass considerations:
- Limited IM injection sites: Primarily quadriceps and lumbar epaxial muscles
- Injection volume limits: <1ml per site for small cats (<4kg)
- Needle length importance: Prevents accidental intramuscular injection during subcutaneous dosing
Recommended Needle Specifications by Application:
Subcutaneous Injections (Most Common):
- Optimal gauge: 25G – 27G (0.5mm – 0.4mm)
- Optimal length: 1/2″ to 5/8″ (12.7mm – 16mm)
- Bevel design: Regular bevel (12-degree angle)
- Coating: Silicone or polymer-coated for smooth insertion
- Manufacturer quality indicator: Triple-beveled, laser-sharpened tips reduce insertion force by 30-40%
Intramuscular Injections (Less Frequent):
- Optimal gauge: 23G – 25G (0.6mm – 0.5mm)
- Optimal length: 5/8″ to 1″ (16mm – 25mm)
- Application note: Reserved for specific medications requiring IM route
- Volume limitation: <1ml per injection site
- Manufacturer quality indicator: Thin-wall needle technology maximizes flow rate while minimizing diameter
Fluid Administration:
- Optimal gauge: 18G – 21G (1.2mm – 0.8mm)
- Optimal length: 1″ to 1.5″ (25mm – 38mm)
- Design: Short bevel for controlled tissue penetration
- Material: Surgical-grade stainless steel (typically 304 or 316L)
- Manufacturer quality indicator: Electro-polished interior surface reduces flow resistance
Small/Pediatric Cats (<2kg):
- Recommended upgrade: 28G – 29G ultra-fine needles
- Length adjustment: 1/2″ maximum
- Application: All subcutaneous injections and most vaccines
- Manufacturer consideration: Specialized manufacturing equipment required for consistent quality at these dimensions
Material Quality and Manufacturing Standards
Premium syringe factories distinguish themselves through superior material selection and processing:
Barrel Material Specifications:
Medical-Grade Polypropylene (PP):
- Polymer grade: USP Class VI certified
- Transparency: >90% light transmission for clear visibility
- Chemical resistance: Compatible with alcohols, oils, aqueous solutions
- Sterilization tolerance: Withstands EO gas and gamma radiation without degradation
- Temperature range: -20°C to +121°C operational stability
- Quality verification: Batch testing for heavy metals, plasticizers, and leachables
Medical-Grade Polyethylene (PE):
- Density specification: Low-density (LDPE) for flexible applications
- Biocompatibility: ISO 10993 series compliance
- Applications: Primarily oral/enteral feeding syringes
- Advantages: Greater flexibility, lower cost, excellent for non-sterile reusable designs
Plunger Material Options:
Natural Rubber (Latex):
- Advantages: Excellent sealing properties, cost-effective
- Disadvantages: Latex allergy concerns, protein leaching potential
- Market trend: Declining use in veterinary applications
- Manufacturer recommendation: Avoid for multi-dose vials or sensitive medications
Synthetic Rubber (Latex-Free):
- Material types: Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE), synthetic polyisoprene
- Advantages: Hypoallergenic, consistent compression properties
- Industry standard: Now preferred by leading syringe manufacturers
- Performance: Equivalent or superior sealing with enhanced safety profile
Siliconized Surface Treatment:
- Process: Micro-layer silicone coating on barrel interior and plunger surface
- Benefits: 60-80% reduction in plunger break-loose and glide force
- Quality control: Uniform coating thickness verified via surface analysis
- Result: Smoother, more controlled injection with reduced syringe clogging
Graduation Marking Quality:
Printing Technology:
- Pad printing: Durable ink fused to barrel surface
- Ink composition: Medical-grade, solvent-resistant formulations
- Permanence testing: 100+ autoclave cycles without fading (where applicable)
- Color standards: Black or dark blue for maximum contrast
Accuracy Requirements:
- Volume tolerance: ±5% for graduations <2ml, ±3% for graduations >2ml
- Line width: 0.2mm – 0.3mm for readability without obscuring contents
- Numbering: Every 0.1ml or 0.5ml depending on capacity
- International standards: ISO 8537 for sterile syringes, ISO 7886 series
Quality Assurance from Reputable Syringe Factories:
Critical manufacturing checkpoints:
- Incoming material inspection (chemical composition, impurities)
- In-process dimensional verification (automated optical inspection)
- Plunger break-loose force testing (typically 8-15 Newtons maximum)
- Leak testing under vacuum and pressure conditions
- Sterility assurance level (SAL) validation: 10^-6 for sterile products
- Bioburden testing for pre-sterilization microbial load
- Package integrity testing (dye penetration, vacuum decay)
Choosing Reliable Syringe Suppliers: A Procurement Guide
For veterinary clinics, pet owners, and distributors seeking quality medical syringes, understanding supplier evaluation criteria is essential.
Manufacturer Certification and Regulatory Compliance
Essential Certifications for Syringe Manufacturing Companies:
ISO 13485:2016 Medical Device Quality Management System:
- Scope: Covers design, production, installation, and servicing of medical devices
- Audit frequency: Annual surveillance with full recertification every 3 years
- Key requirements: Risk management, traceability, validation protocols
- Verification: Request current certificate with accreditation body verification
- Red flag: Certificates older than 12 months or from non-accredited certification bodies
FDA Registration and Listing (United States Market):
- Facility registration: All syringe factories must register with FDA
- Device listing: Each syringe product must be listed with FDA Device Registration
- Establishment Inspection: FDA may conduct unannounced GMP inspections
- 510(k) clearance: Required for new syringe designs claiming equivalence
- Verification method: Search FDA Device Registration database using FEI number
- Importance: Non-registered facilities cannot legally sell in U.S. market
CE Marking (European Economic Area):
- Regulatory framework: Medical Device Regulation (MDR) 2017/745
- Classification: Syringes typically Class IIa or IIb devices
- Conformity assessment: Requires Notified Body involvement for Class IIa and higher
- Technical documentation: Comprehensive design history file required
- Post-market surveillance: Mandatory incident reporting and periodic safety updates
- Critical verification: Request EC Certificate of Conformity and Notified Body details
Additional International Certifications:
- Health Canada Medical Device License (Canada)
- TGA registration (Australia)
- PMDA approval (Japan)
- NMPA registration (China)
- ANVISA certification (Brazil)
- COFEPRIS approval (Mexico)
Production Capacity and Technical Capabilities
Evaluating Syringe Factory Infrastructure:
Annual Production Volume:
- Small manufacturers: 10-50 million units/year
- Medium manufacturers: 50-500 million units/year
- Large manufacturers: 500 million – 2 billion+ units/year
- Relevance: Higher volumes typically indicate established processes and economies of scale
- Consideration: Ensure factory has sufficient capacity to fulfill your volume requirements without compromising quality
Cleanroom Classification:
- Regulatory requirement: ISO 14644-1 Class 7 or 8 for syringe assembly
- Air changes per hour: Minimum 20 for Class 8, 60+ for Class 7
- Particle count monitoring: Continuous airborne particulate measurement
- Gowning protocols: Full cleanroom attire with documented training
- Quality indicator: Ask for cleanroom validation reports and particle count data
Injection Molding Capabilities:
- Machine precision: Tolerance capabilities of ±0.01mm for critical dimensions
- Mold maintenance: Preventive maintenance schedule and mold lifespan tracking
- Process validation: Statistical process control (SPC) with capability indices (Cpk >1.33)
- Cycle time optimization: Balance between productivity and part quality
- Advanced capability: In-house mold design and fabrication for custom requirements
Sterilization Facilities:
- On-site capability: Own sterilization equipment versus outsourcing
- Method options: Ethylene oxide (EO), gamma radiation, e-beam, steam (autoclaving for reusables)
- Validation status: Documented sterilization cycle validation per ISO 11135 or ISO 11137
- Sterility assurance: Biological indicator testing with every cycle
- Advantage: On-site sterilization provides better quality control and faster turnaround
Testing and Quality Control Laboratory:
- Equipment inventory: Tensile testers, dimensional measurement systems, chemical analyzers
- Testing protocols: Physical, chemical, and biological testing per ISO standards
- Staff qualifications: Trained quality control technicians and engineers
- Accreditation: ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation for testing laboratories (preferred)
- Transparency: Reputable manufacturers provide Certificates of Analysis (CoA) with shipments
Product Line Comprehensiveness
Assessing Syringe Manufacturer Product Range:
Capacity Variety: A comprehensive veterinary syringe supplier should offer:
- Ultra-low volume: 0.3ml, 0.5ml (insulin-type)
- Small volume: 1ml, 2ml, 3ml
- Medium volume: 5ml, 10ml, 12ml
- Large volume: 20ml, 30ml, 50ml, 60ml
- Benefit: Single-source supply simplifies procurement and ensures consistent quality standards
Needle Options:
- Gauge range: 18G through 31G
- Length options: 3/8″ through 1.5″ (10mm – 38mm)
- Bevel types: Regular, short, intradermal
- Special features: Safety-engineered, retractable, ultra-thin wall
- Integration: Pre-attached needle-syringe combinations versus separate components
Specialty Products:
- Luer-lock versus slip-tip syringes
- Eccentric or concentric tip designs
- Catheter-tip syringes for enteral feeding
- Control syringes for contrast media
- Prefilled syringe systems
- Innovation indicator: Custom designs show manufacturer responsiveness to market needs
Packaging Configurations:
- Individual sterile pouches (peel-packs)
- Bulk non-sterile packaging for clinic use
- Blister packs for retail/e-commerce
- Multi-pack configurations (10, 20, 50, 100 count)
- Private label and custom branding options
- Consideration: Packaging should match your distribution channel requirements
Pricing Structure and Supply Chain Reliability
Understanding Syringe Manufacturing Economics:
Direct Factory Pricing Advantages:
- Elimination of distributor markups (typically 30-60% premium)
- Volume-based tier pricing for large orders
- Negotiable payment terms (Net 30, Net 60, Letter of Credit)
- Container load discounts for importers
- Cost savings: Direct sourcing can reduce per-unit costs by 40-70%
Total Cost of Ownership Considerations: Beyond unit price, evaluate:
- Shipping and logistics costs (FOB, CIF, DDP terms)
- Import duties and customs clearance fees
- Quality defect rates and return/replacement policies
- Inventory carrying costs and minimum order quantities
- Risk assessment: Ultra-low pricing may indicate quality compromises
Supply Chain Stability Factors:
- Manufacturing lead times (typically 30-90 days for bulk orders)
- Raw material sourcing strategy and supplier diversification
- Inventory buffer for fast-moving SKUs
- Geographic factory locations and geopolitical risk
- Business continuity and disaster recovery plans
- Pandemic lessons: COVID-19 highlighted critical importance of supply chain resilience
Quality Documentation and Traceability:
Essential Documents from Syringe Manufacturers:
- Certificate of Analysis (CoA): Batch-specific test results
- Certificate of Conformity: Declaration of regulatory compliance
- Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS/SDS): For all materials
- Sterilization certificates: Validation and cycle records
- ISO certificates: Current quality system certification
- Biocompatibility reports: ISO 10993 testing summaries
- Product specifications: Detailed dimensional and performance parameters
Traceability Systems:
- Lot numbering and batch tracking
- Production date and expiration date marking
- Barcode or QR code implementation
- Electronic batch records accessible to customers
- Regulatory requirement: Essential for recall management and post-market surveillance
Safe At-Home Injection Techniques: Veterinary Best Practices
For cat owners administering injections under veterinary supervision, proper technique ensures both safety and efficacy.
Pre-Injection Preparation Protocol
Medical Supply Checklist:
Before beginning any injection procedure, gather all necessary items from your veterinary syringe supplier:
Primary Supplies:
- Appropriate-sized sterile disposable syringe (verify intact packaging)
- Correct gauge and length needle (if separate from syringe)
- Prescribed medication (verify name, concentration, and expiration date)
- Alcohol swabs or cotton balls with 70% isopropyl alcohol
- Medical examination gloves (nitrile or vinyl, latex-free preferred)
- Sharps disposal container (FDA-cleared, puncture-resistant)
Optional but Recommended:
- Clean towel or blanket for cat restraint
- Treats or favorite toy for positive reinforcement
- Timer or clock for monitoring injection intervals
- Treatment log book for record keeping
- Emergency veterinary clinic contact information
Medication Preparation Steps:
Step 1: Verify prescription details
- Confirm medication name matches veterinary prescription
- Check concentration (mg/ml) to calculate correct volume
- Verify expiration date is current
- Inspect for discoloration, particles, or cloudiness
- Critical: Never use medication that appears abnormal
Step 2: Hand hygiene
- Wash hands thoroughly with soap and warm water for minimum 20 seconds
- Dry completely with clean towel
- Don medical gloves to maintain aseptic technique
- Infection prevention: Proper hand hygiene reduces contamination risk by >90%
Step 3: Syringe preparation
- Remove sterile syringe from packaging, touching only the barrel
- Attach needle securely (Luer-lock or slip-tip connection)
- Remove needle cap, maintaining needle sterility
- Draw air into syringe equal to medication dose volume
- Purpose: Air injection equalizes vial pressure for easier withdrawal
Step 4: Medication withdrawal
- Clean vial rubber stopper with alcohol swab
- Insert needle through stopper at 90-degree angle
- Inject air into vial
- Invert vial and withdraw prescribed medication volume
- Tap syringe barrel to dislodge air bubbles
- Expel air bubbles by gently pushing plunger until medication reaches needle hub
- Accuracy check: Verify final volume against dosing calculation
Injection Administration Techniques
Subcutaneous Injection Method (Most Common for Cats):
Anatomical Site Selection:
- Preferred location: Scruff region (loose skin between shoulder blades)
- Alternative sites: Lateral thorax, flank region
- Site rotation: Vary location for multiple injections to prevent scar tissue
- Avoid: Areas with limited subcutaneous tissue, joints, spine
Restraint and Positioning:
- Calm environment: Quiet room with minimal distractions
- Handler positioning: One person restrains while another injects (two-person technique ideal)
- Gentle restraint: Towel wrapping or scruffing without excessive force
- Cat comfort: Some cats tolerate injections better on familiar surfaces (favorite bed, owner’s lap)
- Stress reduction: Speak softly and provide reassurance throughout
Injection Procedure:
Step 1: Skin preparation
- Part fur to visualize skin
- Wipe injection site with alcohol swab in circular motion
- Allow alcohol to air dry (30 seconds) to minimize stinging
- Alternative: Some veterinarians consider alcohol prep optional for subcutaneous injections in clean home environments
Step 2: Tent the skin
- Grasp loose skin between thumb and forefinger
- Gently pull upward creating a “tent” of subcutaneous space
- Avoid squeezing too tightly (restricts needle insertion and increases discomfort)
Step 3: Needle insertion
- Hold syringe like a pencil or dart (dominant hand)
- Insert needle at 45-degree angle into base of skin tent
- Use swift, confident motion (hesitation increases pain perception)
- Advance needle 1/4″ to 1/2″ into subcutaneous space
- Depth verification: Needle should move freely within subcutaneous tissue
Step 4: Aspiration (context-dependent)
- Pull back slightly on plunger
- Check for blood return (indicates vein penetration)
- If blood appears: Withdraw needle, select new site
- Note: Many veterinarians no longer recommend aspiration for subcutaneous injections
Step 5: Medication injection
- Depress plunger slowly and steadily (3-5 seconds for small volumes)
- Maintain skin tent throughout injection
- Observation: Watch for swelling at injection site indicating proper subcutaneous placement
Step 6: Withdrawal and post-injection care
- Remove needle smoothly using same angle as insertion
- Release skin tent
- Gently massage injection site (5-10 seconds) to distribute medication
- Observe cat for immediate adverse reactions
- Praise and reward: Offer treats and affection immediately
Intramuscular Injection Method (Less Common, Veterinary Guidance Essential):
Site Selection:
- Preferred: Quadriceps muscles (front of hind leg)
- Alternative: Lumbar epaxial muscles (alongside spine)
- Warning: Improper IM injection can cause muscle damage or sciatic nerve injury
Key Differences from Subcutaneous:
- Needle angle: 90 degrees perpendicular to muscle
- Aspiration: Mandatory to avoid intravascular injection
- Volume limits: <1ml per site for average-sized cats
- Needle gauge: Slightly larger (23G-25G) for thicker muscle tissue
Fluid Therapy Administration (Subcutaneous):
Large-Volume Injection Considerations:
- Typical volume: 50-150ml per session
- Administration rate: 1-2 minutes per 10ml for comfort
- Multiple sites: Divide large volumes between 2-3 injection sites
- Fluid warming: Room temperature fluids better tolerated than refrigerated
- Post-procedure: Fluid “bulge” under skin is normal, absorbs within 6-12 hours
Post-Injection Monitoring and Safety
Immediate Observation Period (First 15-30 Minutes):
Normal Reactions:
- Mild discomfort or sensitivity at injection site
- Brief vocalization during injection
- Temporary reduction in activity
- Small amount of clear fluid leakage from injection site
Abnormal Reactions Requiring Veterinary Contact:
- Facial swelling or hives (allergic reaction)
- Difficulty breathing or open-mouth breathing
- Vomiting or diarrhea within 30 minutes
- Extreme lethargy or collapse
- Seizures or abnormal neurological signs
- Persistent bleeding from injection site
- Emergency response: Contact veterinarian or emergency clinic immediately
Injection Site Assessment (Days 1-7):
Normal Healing:
- Slight redness or warmth at site (resolves within 24-48 hours)
- Small, firm lump (sterile inflammatory response, typically resolves within 1 week)
- Minimal hair loss at site
Concerning Signs:
- Increasing swelling, heat, or pain
- Discharge (pus) from injection site
- Wound opening or tissue breakdown
- Fever or systemic illness
- Infection indicators: Require veterinary examination and possible antibiotic therapy
Sharps Disposal and Medical Waste Management
Proper Disposal of Used Syringes:
FDA-Cleared Sharps Containers:
- Specifications: Puncture-resistant, leak-proof, closeable lid
- Labeling: Clear biohazard symbol and “SHARPS” marking
- Size options: 1-quart to multi-gallon capacities
- Fill level: Never fill beyond marked line (typically 3/4 full)
- Availability: Purchase from pharmacies, medical supply companies, or veterinary syringe suppliers
Temporary Disposal (if sharps container unavailable):
- Heavy-duty plastic container with screw-top lid (laundry detergent bottle)
- Label clearly: “SHARPS – DO NOT RECYCLE”
- Secure lid with heavy-duty tape before disposal
- Never use: Glass containers, thin plastic bottles, coffee cans, or paper containers
Final Disposal Methods:
- Community sharps disposal programs (check local waste management)
- Mail-back programs (sharps container with prepaid shipping)
- Collection sites at pharmacies or hospitals
- Household hazardous waste facilities
- Important: NEVER place sharps in regular trash or recycling bins
State and Local Regulations: Different jurisdictions have varying requirements for home sharps disposal. Consult:
- Local health department
- Waste management district
- State environmental protection agency
- Resources: EPA website (epa.gov) provides state-specific guidance
Advanced Considerations: Specialized Syringe Applications
Insulin Administration for Diabetic Cats
Diabetes Mellitus in Felines:
Feline diabetes affects approximately 0.5-2% of the cat population, with increasing prevalence due to obesity and sedentary lifestyles. Diabetic cats require twice-daily insulin injections, making proper insulin syringe selection critical for long-term management success.
Insulin Syringe Specifications:
U-100 Insulin Syringes (Most Common):
- Concentration match: Designed for U-100 insulin (100 units per ml)
- Capacity options: 0.3ml (30 units), 0.5ml (50 units), 1ml (100 units)
- Graduation increments: 1-unit or 2-unit markings
- Needle specifications: 29G-31G × 5/16″ to 1/2″ (0.33mm-0.25mm × 8-12.7mm)
- Critical: Always match syringe type to insulin concentration to prevent dosing errors
U-40 Insulin Syringes (Veterinary-Specific):
- Application: ProZinc and some compounded veterinary insulins
- Concentration: 40 units per ml
- Distinct color coding: Often red or orange cap/plunger to differentiate from U-100
- Warning: Using U-100 syringe with U-40 insulin results in 2.5× overdose
- Availability: Specialized veterinary syringe manufacturers produce these lower-concentration syringes
Pen Needles for Insulin Pens:
- Compatibility: VetPen, other veterinary insulin delivery systems
- Specifications: 29G-32G × 5mm-8mm
- Advantages: Pre-filled cartridge convenience, dose dial accuracy
- Cost consideration: Higher per-dose cost but improved owner compliance
Best Practices for Diabetic Cat Insulin Injection:
- Administration timing: 12-hour intervals aligned with feeding schedule
- Site rotation: Alternate between left and right lateral thorax
- Storage: Refrigerate unopened vials, room temperature in-use vials (up to 28 days)
- Needle replacement: New sterile needle every injection (never reuse)
- Blood glucose monitoring: Periodic testing to adjust insulin dosage
- Hypoglycemia awareness: Know signs of low blood sugar (weakness, seizures, collapse)
Compounded Medication Administration
Custom Veterinary Pharmacy Solutions:
Veterinary compounding pharmacies create customized medications in forms and concentrations not commercially available. These specialized formulations often require specific syringe types from experienced medical syringe suppliers.
Common Compounded Injectable Medications:
- Transdermal medications in lipophilic bases
- Concentrated pain medications (buprenorphine, morphine)
- Chemotherapy agents for cancer treatment
- Appetite stimulants (mirtazapine, maropitant)
- Antiemetics and GI medications
- Storage requirements: Often require refrigeration and light protection
Syringe Selection for Compounded Drugs:
- Chemical compatibility: Verify syringe material compatible with medication vehicle
- Accurate graduations: Compounded meds often require precise small-volume dosing
- Preservative concerns: Some formulations lack preservatives, requiring single-use syringes
- Stability considerations: Draw medication immediately before administration
- Pharmacist guidance: Always follow compounding pharmacy instructions precisely
Oil-Based vs. Aqueous Formulations:
- Oil-based: May require larger needle gauge (23G-25G) due to higher viscosity
- Aqueous solutions: Standard needle gauges (25G-27G) typically adequate
- Suspension medications: Gentle mixing required before drawing into syringe
- Viscosity challenges: Some syringe manufacturing companies produce specialized high-viscosity syringes
Vaccine Administration and Cold Chain Management
Feline Core and Non-Core Vaccines:
Core Vaccines (Recommended for All Cats):
- FVRCP (Feline Viral Rhinotracheitis, Calicivirus, Panleukopenia)
- Initial series: 3 doses starting at 6-8 weeks
- Boosters: Every 1-3 years based on protocol
- Volume: 1ml subcutaneous
- Rabies Vaccine
- Initial: Single dose at 12-16 weeks
- Boosters: Annual or triennial based on product
- Volume: 1ml subcutaneous or intramuscular
- Legal requirement: Mandated in most jurisdictions
Non-Core Vaccines (Risk-Based):
- FeLV (Feline Leukemia Virus): 1ml subcutaneous series
- Bordetella: 1ml intranasal or subcutaneous
- Chlamydia: Included in some FVRCP combinations
Vaccine-Specific Syringe Requirements:
Pre-filled Syringe Systems:
- Single-dose presentation: Vaccine and diluent in separate chambers
- Activation mechanism: Twist or push to mix components
- Advantages: Eliminates reconstitution errors, maintains sterility
- Manufacturers: Major veterinary pharmaceutical companies provide proprietary systems
Standard Multi-Dose Vials:
- Reconstitution required: Mix lyophilized vaccine with sterile diluent
- Syringe specifications: 1ml or 3ml standard syringes with 20G-22G drawing needle
- Administration needle: Switch to 25G-27G for injection
- Best practice: Use separate syringe for each animal to prevent cross-contamination
Cold Chain Integrity:
- Temperature monitoring: Vaccines must maintain 2-8°C (36-46°F)
- Transport considerations: Insulated containers with ice packs
- Syringe implications: Do not pre-draw vaccines for later administration
- Stability concerns: Reconstituted vaccines typically stable <2 hours
- Quality assurance: Temperature excursions may render vaccines ineffective
Vaccine-Associated Sarcoma Prevention
Feline Injection-Site Sarcoma (FISS):
Vaccine-associated sarcomas are rare (1 in 10,000 to 1 in 30,000 vaccinated cats) but aggressive tumors potentially linked to injection-site inflammation.
Risk Reduction Strategies:
- Anatomical site selection: Vaccinate in locations amenable to wide surgical excision
- Recommended sites: Distal limbs (below elbow/stifle) or tail base
- Avoid: Interscapular region (traditional site but poor surgical access)
- Vaccine type selection: Non-adjuvanted vaccines when available
- Vaccination frequency: Follow minimum necessary protocol (3-year core vaccines)
- Needle gauge consideration: Some evidence suggests smaller needles reduce inflammation
- Documentation: Record specific injection sites in medical record
Syringe and Needle Quality Impact:
- Needle sharpness: Dull or damaged needles increase tissue trauma
- Multiple tissue passes: Avoid redirecting needle through tissue
- Injection speed: Slow, controlled injection minimizes tissue disruption
- Manufacturing quality: Premium syringe factories maintain strict needle sharpness standards
Post-Vaccination Monitoring:
- Normal reactions: Small, soft swelling resolving within 1-2 weeks
- Concerning masses: Firm nodule persisting >3 months, growing after 1 month, or >2cm diameter
- “3-2-1 Rule”: Biopsy any mass that persists 3 months, grows after 1 month, or exceeds 2cm
- Early detection: Significantly improves surgical outcome
Emerging Technologies in Veterinary Syringe Manufacturing
Safety-Engineered Syringes
Needlestick Injury Prevention:
Healthcare workers, including veterinary professionals, face significant needlestick injury risk. The U.S. Needlestick Safety and Prevention Act (2000) mandates safety-engineered devices in human medicine, driving innovation adopted by veterinary syringe manufacturers.
Retractable Needle Syringes:
- Mechanism: Spring-loaded system retracts needle into barrel after injection
- Activation: Automatic upon complete plunger depression or manual button press
- Advantages: Immediate needle containment, reduces sharps disposal volume
- Limitations: Higher cost (3-5× standard syringes), learning curve for proper use
- Veterinary adoption: Growing use in high-volume vaccination clinics
Protective Sheath Systems:
- Design: Sliding plastic shield covers needle after use
- Activation: One-handed technique using table edge or finger
- Standards compliance: OSHA bloodborne pathogens standard
- Cost: Moderate premium over standard syringes
- Best for: Practices with high employee turnover or training emphasis
Fixed-Needle Safety Syringes:
- Configuration: Needle permanently attached to barrel
- Safety feature: Needle retracts or shields after injection
- Applications: Primarily human medicine vaccines, limited veterinary use
- Consideration: Not suitable for medication drawing from vials
Market Trends: Leading syringe manufacturing companies report 15-20% annual growth in safety-engineered product lines as veterinary practices prioritize employee safety and OSHA compliance.
Auto-Disable and Single-Use Syringes
WHO Global Vaccination Safety Initiative:
Auto-disable (AD) syringes prevent reuse through mechanical lockout after single use, critical in developing regions but gaining veterinary applications.
Mechanism Types:
- Plunger lockout: After complete depression, plunger cannot be withdrawn
- Barrel breach: Plunger breaks through barrel base, rendering syringe unusable
- Fixed-dose volume: Pre-set volume prevents overfilling or reuse
- Primary market: Mass vaccination campaigns (rabies control, TNR programs)
Veterinary Applications:
- Shelter medicine: High-volume spay/neuter and vaccination clinics
- Wildlife vaccination: Oral rabies vaccine programs
- Developing regions: Feral cat management and zoonotic disease control
- Cost factor: Slightly higher than standard syringes but prevents cross-contamination risks
Prefilled Syringe Systems
Pharmaceutical Industry Evolution:
Prefilled syringes represent the fastest-growing segment in both human and veterinary pharmaceuticals, with specialized syringe manufacturers investing heavily in sterile filling capabilities.
Advantages Over Multi-Dose Vials:
- Dosing accuracy: Eliminates measurement errors
- Reduced waste: No overfill or unused medication
- Contamination prevention: Closed system maintains sterility
- Convenience: Ready-to-use with no reconstitution
- Stability: Glass syringes provide superior barrier properties
- Owner compliance: Simplifies at-home administration
Technical Challenges:
- Drug compatibility: Must evaluate drug-syringe material interactions
- Silicone lubrication: Can cause protein aggregation in biologics
- Glass delamination: Borosilicate glass quality critical
- Regulatory approval: Complex validation and stability testing required
- Manufacturing expertise: Requires pharmaceutical-grade cleanroom facilities (ISO Class 7 or better)
Current Veterinary Prefilled Products:
- Convenia (cefovecin): Long-acting antibiotic injection
- Solensia (frunevetmab): Monoclonal antibody for osteoarthritis pain
- Librela (bedinvetmab): Canine osteoarthritis treatment (potential feline formulation)
- Various emergency medications: Epinephrine, dexamethasone
- Market expansion: Expected to grow 25-30% annually through 2030
Smart Syringes and Digital Health Integration
Connected Medical Devices:
Emerging syringe technology incorporates digital features enabling dose tracking, compliance monitoring, and data integration with veterinary practice management systems.
Smart Syringe Features:
- Dose sensors: Electronic verification of administered volume
- RFID/NFC tags: Track individual syringe usage and medication lot numbers
- Mobile app connectivity: Bluetooth transmission to smartphone applications
- Cloud integration: Upload injection data to veterinary health records
- Reminder systems: Alerts for scheduled injections
- Target users: Chronic disease management (diabetes, kidney disease)
Benefits for Diabetic Cat Management:
- Dose logging: Automatic record of insulin dose and timing
- Pattern recognition: Software identifies trends in glucose control
- Compliance improvement: Studies show 30-40% better adherence with digital tracking
- Veterinary oversight: Clinicians review injection data remotely
- Challenges: Higher device cost, technology adoption barriers for some owners
Regulatory Landscape:
- FDA digital health guidance: Software as Medical Device (SaMD) framework
- Data privacy: HIPAA considerations for veterinary applications
- Interoperability: Lack of industry standards for data exchange
- Market maturity: Still emerging, primarily in human medicine with veterinary applications in development
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Medical Waste Burden of Disposable Syringes
Global Plastic Medical Waste Crisis:
The medical device industry, including syringe manufacturers, generates approximately 2 million tons of plastic waste annually worldwide. Disposable syringes constitute a significant portion of this waste stream.
Environmental Impact Metrics:
- Average syringe weight: 4-8 grams (primarily polypropylene)
- Global annual production: 16-20 billion syringes
- Waste generation: 64,000-160,000 tons plastic waste annually
- Landfill concerns: Non-biodegradable, 450+ year decomposition timeline
- Incineration emissions: CO2, dioxins, and furans from medical waste burning
Veterinary Contribution:
- Estimated veterinary syringe use: 400-600 million units annually (U.S. alone)
- Practice waste volume: Average small animal clinic generates 10-20 pounds sharps waste monthly
- Disposal costs: Rising sharps disposal fees ($15-50 per sharps container)
- Growing awareness: Veterinary professionals increasingly seeking sustainable alternatives
Sustainable Syringe Innovations
Bio-Based and Biodegradable Polymers:
Progressive syringe manufacturing companies are exploring alternative materials to reduce environmental footprint:
Polylactic Acid (PLA) Syringes:
- Material source: Derived from corn starch or sugarcane
- Biodegradability: Compostable under industrial conditions (180 days)
- Performance: Comparable clarity and strength to polypropylene
- Sterilization: Compatible with EO and gamma radiation
- Limitations: Higher material cost, limited production scale, not yet approved for all medical applications
Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA):
- Production: Bacterial fermentation of plant oils or sugars
- Properties: Fully biodegradable in marine and soil environments
- Medical-grade quality: Biocompatible and sterilizable
- Market status: Pilot-scale production, limited commercial availability
- Potential: Next-generation sustainable medical plastics
Recycling Initiatives:
- Closed-loop programs: Some syringe factories accept clean, unused syringes for reprocessing
- Chemical recycling: Advanced pyrolysis breaks down plastics to base chemicals
- Challenges: Contamination concerns, regulatory hurdles for medical device recycling
- Current reality: <5% of medical plastics recycled globally
Reusable Glass Syringes
Historical Context and Modern Revival:
Before disposable plastic syringes became standard in the 1960s, glass and metal syringes were sterilized and reused. Some veterinary practices and sustainable healthcare advocates are revisiting reusable systems.
Modern Reusable Syringe Systems:
- Construction: Borosilicate glass barrel with stainless steel or PTFE plunger
- Capacity range: Typically 2ml, 5ml, 10ml, 20ml
- Sterilization: Autoclavable at 121°C (250°F) for 15-30 minutes
- Lifespan: 100-500+ sterilization cycles with proper care
- Cost analysis: Higher upfront cost but lower long-term per-use expense
Advantages:
- Environmental: Dramatic waste reduction (99% fewer disposables)
- Chemical inertness: Glass provides superior compatibility with wide range of medications
- Precision: Metal components maintain tight tolerances over many uses
- Economics: Break-even typically achieved within 50-100 uses
- Quality perception: Some practitioners prefer tactile feel and control of glass
Disadvantages and Limitations:
- Breakage risk: Glass fracture during handling or sterilization
- Labor requirements: Cleaning, inspection, and sterilization labor-intensive
- Contamination concerns: Risk of incomplete cleaning or sterilization failure
- Regulatory compliance: Must validate cleaning and sterilization protocols
- Needle disposal: Still requires disposable needles and sharps containers
Best Applications for Reusable Syringes:
- Compounding pharmacies: Frequent medication preparation
- Fluid therapy: Large-volume subcutaneous administration
- Multi-dose vial drawing: Medication withdrawal without patient contact
- Not recommended: Direct patient injection (infection control concerns)
Manufacturer Sustainability Commitments
Corporate Social Responsibility in Syringe Manufacturing:
Leading medical device manufacturers are implementing comprehensive sustainability programs:
Carbon Footprint Reduction:
- Renewable energy: Solar panels and wind power for manufacturing facilities
- Energy efficiency: LED lighting, optimized HVAC systems, waste heat recovery
- Transportation optimization: Regional distribution centers reducing shipping distances
- Targets: Many manufacturers committed to carbon neutrality by 2030-2040
Sustainable Sourcing:
- Raw material selection: Priority for bio-based or recycled polymers where feasible
- Supplier audits: Environmental and social responsibility verification
- Local sourcing: Reduced transportation emissions and supply chain resilience
- Certifications: ISO 14001 environmental management systems
Waste Minimization:
- Manufacturing scrap reduction: Process optimization minimizing material waste
- Regrind programs: Internal recycling of clean production scrap
- Packaging reduction: Minimalist designs using recycled cardboard
- Circular economy: Designing products with end-of-life considerations
Water Conservation:
- Closed-loop cooling systems: Minimal water consumption in injection molding
- Wastewater treatment: On-site treatment and reuse of process water
- Metrics: Leading facilities reduce water usage by 40-60% versus industry averages
Regulatory Compliance and Quality Standards for International Markets
United States Regulatory Framework
FDA Medical Device Regulation:
All syringe manufacturers selling products in the United States must comply with comprehensive Food and Drug Administration oversight.
Device Classification:
- Class II Medical Device: Most syringes classified as Class II
- Regulatory controls: General controls + special controls (performance standards)
- Premarket notification: 510(k) clearance required demonstrating substantial equivalence
- Establishment registration: Annual registration and device listing
- Exempt categories: Certain veterinary syringes may qualify for exemptions
Quality System Regulation (QSR):
- 21 CFR Part 820: Codified Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
- Key requirements:
- Management responsibility and quality planning
- Design controls (for devices not exempt)
- Document and change controls
- Purchasing controls and supplier evaluation
- Production and process controls
- Equipment maintenance and calibration
- Complaint handling and adverse event reporting
- Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) systems
- Inspection frequency: FDA typically inspects facilities every 2-3 years
Veterinary Device Regulations:
- Simplified pathway: Veterinary devices often have less stringent requirements than human devices
- Veterinary Feed Directive (VFD): Some implantable or medicated devices require VFD
- Off-label use: Veterinarians have greater flexibility for off-label product use
- Market advantage: Some manufacturers produce “dual-use” syringes suitable for both human and veterinary applications
European Union Medical Device Regulation
MDR 2017/745 Comprehensive Framework:
The European Medical Device Regulation, fully effective May 2021, significantly increased requirements for medical syringe suppliers in EU markets.
Key MDR Requirements:
Device Classification:
- Rule 5 application: Syringes classified as Class IIa (sterile) or Class I (non-sterile)
- Risk-based approach: Classification based on invasiveness, duration, and body contact
- Class IIa implications: Requires Notified Body involvement for conformity assessment
Technical Documentation:
- Device description: Detailed specifications, materials, manufacturing processes
- Clinical evaluation: Systematic literature review and clinical data analysis
- Risk management: ISO 14971 comprehensive risk assessment
- Post-market surveillance plan: Active monitoring of field performance
- Periodic Safety Update Report (PSUR): Regular safety reporting to authorities
- Documentation depth: Typically 500-2000+ pages for syringe product families
Notified Body Assessment:
- Selection: Choose EU-designated Notified Body for conformity assessment
- Quality system audit: Comprehensive facility and system evaluation
- Technical documentation review: Detailed examination of all submission materials
- Surveillance: Annual or biennial follow-up assessments
- Timeline: Initial approval typically 6-18 months depending on complexity
Unique Device Identification (UDI):
- Mandatory labeling: Machine-readable UDI code on all products
- Database registration: Entry in European Database on Medical Devices (EUDAMED)
- Traceability: Supply chain tracking from manufacturer to end user
- Implementation phases: Rolled out by device class through 2027
Authorized Representative:
- EU requirement: Non-EU manufacturers must designate EU-based authorized representative
- Responsibilities: Acts as liaison with authorities, maintains technical documentation
- Selection criteria: Choose experienced representative familiar with medical device regulations
Other Major International Markets
Health Canada (Canada):
- Medical Device Regulations (SOR/98-282)
- Risk-based classification: Similar to EU system (Class I-IV)
- Medical Device License required for Class II-IV
- Establishment License for manufacturers and importers
- Canadian Medical Devices Conformity Assessment System (CMDCAS)
- Processing time: 60-90 days for routine Class II devices
Therapeutic Goods Administration (Australia):
- Therapeutic Goods Act 1989
- Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG)
- Conformity assessment: Can leverage EU CE marking for most devices
- Sponsor requirements: Australian entity must be registered sponsor
- Market access: Relatively streamlined for CE-marked devices
Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (Japan):
- Pharmaceutical Affairs Law (PAL)
- Pre-market approval: Generally required, cannot leverage other approvals
- Clinical data: May require Japan-specific clinical evaluation
- Registered overseas manufacturer: Foreign manufacturers must register
- Complexity: Considered one of most challenging regulatory environments
National Medical Products Administration (China):
- Medical Device Regulations
- Classification: Class I (lowest risk) to Class III (highest risk)
- Registration process: Comprehensive technical review and facility inspection
- Clinical trials: Often required even for predicate devices
- Local agent: Chinese registration holder required
- Timeline: 1-3 years typical for foreign manufacturers
Regulatory Strategy for Global Syringe Manufacturers:
- Primary approval: Often pursue FDA or CE marking first
- Mutual recognition: Leverage initial approvals for subsequent markets
- Regional distribution: Partner with established distributors for regulatory navigation
- Documentation management: Maintain centralized system for global submissions
- Ongoing compliance: Monitor regulatory changes across all markets
Future Trends in Veterinary Syringe Technology
Precision Dosing and Microfluidics
Nanoliter-Scale Drug Delivery:
Emerging therapies, including biologics and gene therapies, require unprecedented dosing precision. Advanced syringe manufacturers are developing microfluidic devices capable of nanoliter (10⁻⁹ liter) accuracy.
Applications in Veterinary Medicine:
- Expensive biologics: Monoclonal antibodies, recombinant proteins
- Gene therapy: Precise vector dosing critical for efficacy and safety
- Chemotherapy: Narrow therapeutic windows require exact dosing
- Ophthalmologic drugs: Intraocular injections of minute volumes
- Market drivers: Cost containment and improved therapeutic outcomes
Technology Components:
- Microfluidic channels: Precise fluid control through microscale pathways
- Piezoelectric actuators: Electronic control of fluid dispensing
- Optical sensors: Real-time volume measurement and verification
- Manufacturing challenges: Requires semiconductor-level fabrication precision
Needle-Free Injection Systems
Jet Injection Technology:
Needle-free injectors use high-pressure fluid streams to penetrate skin, eliminating needlestick injury risks and needle phobia.
Mechanism:
- Pressure generation: Spring-loaded, compressed gas, or electric actuator
- Fluid stream: 100-200 μm diameter jet penetrates skin at high velocity (>100 m/s)
- Depth control: Pressure and duration determine subcutaneous vs. intramuscular delivery
- Tissue interaction: Creates temporary micropore for drug delivery
Veterinary Applications:
- Mass vaccination: High-throughput vaccination clinics
- Needle-averse animals: Reduces restraint requirements
- Biologics delivery: Some proteins stable under jet injection conditions
- Limitations: Higher equipment cost, drug formulation requirements, potential tissue damage concerns
Current Commercial Systems:
- PharmaJet Stratis: Intramuscular needle-free injection
- ZetaJet: Veterinary-specific system under development
- Research stage: Multiple academic and commercial development programs
Biodegradable Implantable Delivery Systems
Sustained-Release Microsphere Technology:
Some pharmaceutical manufacturers are developing injectable biodegradable microspheres that release medication over weeks to months, potentially delivered via modified syringe systems.
Mechanism:
- Polymer matrix: PLGA (poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid) or similar biocompatible polymers
- Drug encapsulation: Medication dispersed throughout polymer matrix
- Controlled release: Polymer degradation rate determines drug release kinetics
- Elimination: Polymer breaks down to lactic and glycolic acid, naturally metabolized
Veterinary Products:
- Oncept (melanoma vaccine): Sustained antigen release
- Bravecto injection (fluralaner): 12-week parasite protection
- Future applications: Long-acting antibiotics, pain medications, immunomodulators
- Syringe requirements: Larger needle gauges (18G-20G) to accommodate viscous suspensions
Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing Quality Control
Machine Vision and Defect Detection:
Leading syringe factories are implementing AI-powered inspection systems achieving defect detection rates exceeding human inspection.
Technology Components:
- High-resolution cameras: Capture multiple angles of each syringe
- Machine learning algorithms: Trained on millions of images to identify defects
- Real-time processing: Inspection at production speeds (300-600 units/minute)
- Defect categories: Dimensional variations, contamination, printing defects, material flaws
Performance Metrics:
- Detection rate: >99.9% sensitivity for critical defects
- False positive rate: <0.1% (minimizes unnecessary rejection)
- Consistency: Eliminates human fatigue and subjective judgment
- Cost-benefit: System payback typically 12-24 months through reduced waste and recalls
Predictive Maintenance:
- Equipment monitoring: Sensors track injection molding machine parameters
- Predictive algorithms: Identify trends indicating potential equipment failures
- Maintenance scheduling: Proactive maintenance prevents quality issues and downtime
- Outcome: 30-50% reduction in unplanned downtime
Conclusion: Partnering with Quality Syringe Manufacturers for Optimal Feline Care
Selecting appropriate pet cat syringes requires understanding the intersection of feline physiology, medical requirements, manufacturing quality, and regulatory compliance. Whether you’re a veterinary professional, pet owner, or distributor, working with reputable syringe manufacturers ensures access to safe, effective, and reliable injection systems.
Key Takeaways for Veterinary Professionals
Clinical Excellence:
- Match syringe capacity and needle gauge to specific medications and injection routes
- Prioritize manufacturing quality to minimize patient discomfort and adverse reactions
- Stay informed about emerging technologies that may improve patient care
- Implement proper injection techniques to optimize therapeutic outcomes and minimize complications
Practice Management:
- Establish relationships with reliable veterinary syringe suppliers offering consistent quality and supply
- Evaluate total cost of ownership beyond unit price, including disposal costs and staff efficiency
- Consider safety-engineered devices to protect staff and comply with occupational health regulations
- Maintain proper inventory management to prevent expired or compromised supplies
Guidance for Pet Owners
Home Care Responsibilities:
- Use only syringes and needles prescribed or recommended by your veterinarian
- Purchase from reputable medical syringe suppliers ensuring product authenticity and quality
- Never reuse disposable syringes or needles under any circumstances
- Follow proper injection techniques as demonstrated by veterinary staff
- Dispose of sharps safely using approved containers and disposal programs
- Monitor your cat for adverse reactions and maintain communication with your veterinary team
Chronic Disease Management:
- For conditions requiring long-term injections (diabetes, kidney disease), invest in quality supplies
- Consider digital tracking systems to improve compliance and therapeutic monitoring
- Purchase adequate supplies to avoid emergency shortages
- Store medications and supplies according to manufacturer recommendations
Considerations for Distributors and Procurement Specialists
Supplier Selection Criteria:
- Verify regulatory compliance and certifications appropriate for your market
- Assess manufacturing capacity and supply chain reliability
- Evaluate quality management systems and consistency of product specifications
- Review pricing structures and total cost including shipping, handling, and storage
- Investigate customer service capabilities and technical support availability
Market Positioning:
- Understand customer segments: veterinary hospitals, mobile clinics, pet owners, shelters
- Offer product variety meeting diverse clinical needs and budget constraints
- Provide education and training resources supporting proper product use
- Develop value-added services: custom packaging, just-in-time delivery, inventory management
- Build strong partnerships with syringe manufacturing companies for long-term competitive advantage
The Role of Innovation in Advancing Feline Healthcare
The medical syringe industry continues evolving to meet changing healthcare needs. From basic disposable syringes to sophisticated smart delivery systems, innovation driven by quality-focused syringe factories improves patient safety, clinical efficacy, and healthcare sustainability.
Priority areas for continued development:
- Enhanced safety features protecting both patients and healthcare providers
- Sustainable materials and manufacturing processes reducing environmental impact
- Precision dosing technologies supporting expensive biologic medications
- Digital health integration enabling better chronic disease management
- Global access ensuring high-quality products reach underserved markets and veterinary sectors
Final Recommendations
For optimal feline injection therapy:
- Prioritize quality over cost: Premium syringes from reputable syringe manufacturers provide superior performance and safety
- Match products to applications: Understand specific requirements of different medications and injection techniques
- Invest in training: Proper technique is as important as quality equipment
- Maintain regulatory compliance: Ensure all products meet applicable medical device standards
- Consider sustainability: Where possible, choose manufacturers with environmental responsibility commitments
- Stay informed: Medical device technology evolves rapidly; periodically review product options
- Build relationships: Develop partnerships with syringe suppliers who provide technical support and quality assurance
The global market for pet cat syringes continues expanding, driven by growing pet ownership, advancing veterinary medicine, and increasing emphasis on home healthcare. By understanding the complex factors influencing syringe selection—from manufacturing standards to clinical applications—stakeholders across the veterinary healthcare ecosystem can make informed decisions that ultimately benefit feline patients.
Whether administering lifesaving vaccines, managing chronic diseases, or providing comfort care, the humble syringe remains an indispensable tool in feline medicine. Choosing products from certified syringe manufacturing companies committed to quality, safety, and innovation ensures this essential tool performs its critical role effectively.
The intersection of veterinary science, manufacturing excellence, and compassionate care defines the future of feline health—and it begins with selecting the right syringe for every application.