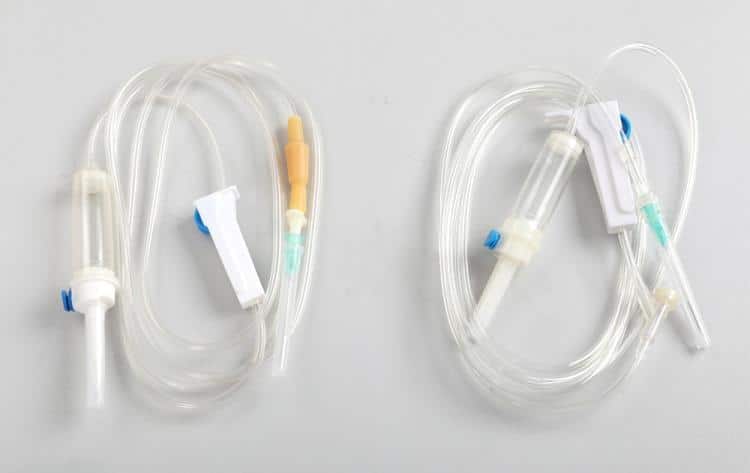
The infusion set, as the core medical device for intravenous infusion therapy, plays an irreplaceable role in modern clinical medicine. This document aims to provide healthcare professionals with systematic guidance on the functional characteristics, operational standards, and quality management of infusion sets to ensure patient safety and enhance treatment outcomes.
1. Structural Components and Basic Functions of Infusion Sets
1.1 Standard Structural Components
Standard disposable infusion sets consist of the following core components:
- Infusion bottle (bag) hook: Supports infusion containers, ensuring stable suspension
- Drip chamber: Controls fluid flow rate, facilitates flow observation
- Infusion tubing: Medical-grade PVC material, typically 150-200cm in length
- Flow rate regulator: Precision control of infusion speed
- Injection port: Facilitates additional medication injection
- Precision filter: Filters foreign particles, typically 5μm or 15μm specifications
- Intravenous needle: Establishes venous access, ranging from 18G to 24G
1.2 Core Functional Characteristics
1.2.1 Precise Flow Rate Control
- Drop factor standard: International standard of 20 drops/mL (adult use) or 60 drops/mL (pediatric use)
- Flow rate calculation formula: Infusion rate (mL/h) = Drops per minute × 60 ÷ Drop factor
- Clinically recommended drop rates:
- Adult routine infusion: 40-60 drops/minute (120-180mL/h)
- Pediatric infusion: Calculated at 4-6mL/kg/h based on body weight
- Elderly patients: Appropriately reduced to 30-40 drops/minute
1.2.2 High-Efficiency Filtration Protection
Modern infusion sets equipped with precision filtration systems can effectively remove:
- Glass particles (>5μm)
- Rubber fragments and plastic particles
- Fibrous foreign matter
- Certain microbial contaminants
1.2.3 Air Embolism Prevention
- Drip chamber fluid level control: Maintained at 1/3 to 2/3 of chamber volume
- Automatic shut-off device: High-end products equipped with automatic stop when fluid is depleted
- Air-elimination design: Effectively prevents air from entering the blood circulation system
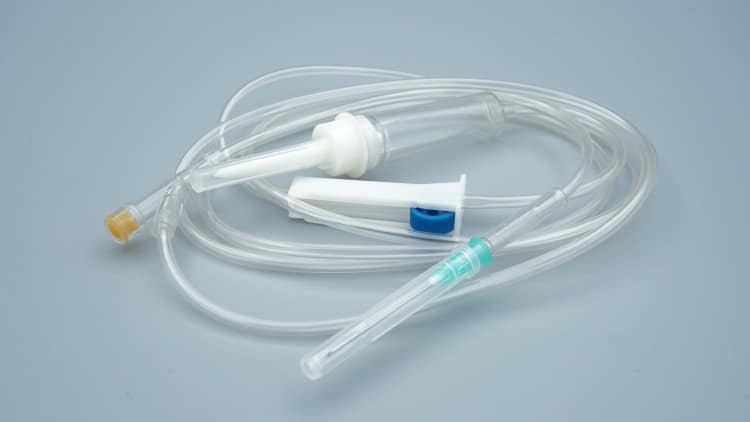
2. Clinical Application Technical Standards
2.1 Sterile Operation Standard Procedures
2.1.1 Pre-use Inspection Points
- Package integrity: Check for damage or moisture in packaging
- Expiration date confirmation: At least 6 months before expiration
- Product identification: Verify batch number, specifications, production date
- Visual inspection: Tubing transparency, connection point tightness
2.1.2 Standard Operating Procedures
Pre-operative preparation → Sterile protection → Equipment inspection →
Establish access → Flow rate setting → Process monitoring →
Complete care → Record documentation
2.2 Clinical Standards for Flow Rate Control
| Patient Type | Weight Range (kg) | Recommended Flow Rate (mL/h) | Special Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neonates | 2.5-4.0 | 10-20 | Strictly calculate by weight |
| Infants/Toddlers | 4-15 | 30-80 | Monitor electrolyte balance |
| Children | 15-40 | 80-200 | Adjust according to condition |
| Adults | >40 | 200-500 | Assess cardiac/renal function |
| Elderly | >65 | 150-300 | Reduce infusion speed |
2.3 Infusion Reaction Monitoring and Management
2.3.1 Common Adverse Reaction Types
- Allergic reactions: Rash, dyspnea, hypotension
- Pyrogenic reactions: Fever, chills, general malaise
- Phlebitis: Pain along venous pathway, erythema, induration
- Fluid overload: Pulmonary edema, cardiac dysfunction
2.3.2 Emergency Response Procedures
- Immediately stop infusion
- Maintain venous access
- Monitor vital signs
- Provide symptomatic treatment
- Detailed documentation and reporting
3. Infusion Set Classification and Selection Guide
3.1 Classification by Function
| Type | Technical Features | Application Range | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Type | Basic filtration, flow control | Routine drug infusion | Economic |
| Precision Type | High-precision filtration, fine flow control | Chemotherapy drugs, blood products | Mid-to-High-end |
| Smart Type | Electronic control, data recording | ICU, operating room applications | High-end |
| Specialized Type | Special materials, customized functions | Special drugs, sensitive patients | Customized |
3.2 Material Safety Considerations
3.2.1 PVC Material Infusion Sets
- Advantages: Low cost, good transparency, excellent flexibility
- Limitations: Contains DEHP plasticizer, may affect certain drug stability
- Applications: Routine water-soluble drug infusion
3.2.2 Non-PVC Material Infusion Sets
- Material types: Polyolefin, silicone, polyurethane, etc.
- Advantages: DEHP-free, better chemical stability
- Applications: Lipid-soluble drugs, pediatric medications, long-term treatment
4. Quality Control and Risk Management
4.1 Product Quality Standards
4.1.1 National Standard Requirements
- Implementation standard: GB 8368-2018 “Disposable Infusion Sets”
- Registration requirements: NMPA registration certificate
- Quality system: ISO 13485 Medical Device Quality Management System
4.1.2 Performance Indicator Requirements
- Flow accuracy: Within ±10%
- Drop factor deviation: Within ±10%
- Filtration efficiency: ≥99.9% (for corresponding particle size)
- Biocompatibility: Compliant with ISO 10993 series standards
4.2 Risk Control Measures
4.2.1 Systematic Risk Prevention and Control
| Risk Type | Occurrence Probability | Harm Severity | Control Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air embolism | Low | High | Strict air elimination, use anti-embolism devices |
| Infection transmission | Medium | High | Sterile operation, single-use only |
| Drug adverse reactions | Medium | Medium | Allergy history inquiry, reaction monitoring |
| Flow rate errors | High | Medium | Double-person verification, electronic monitoring |
4.2.2 Complete Quality Traceability
Establish complete traceability chain from production to use:
- Production phase: Raw material control, process monitoring, finished product inspection
- Distribution phase: Storage conditions, transportation monitoring, expiration management
- Usage phase: Usage records, adverse event reporting, effectiveness evaluation
5. Technology Development Trends and Prospects
5.1 Intelligent Development Directions
- IoT integration: Internet of Things technology for remote monitoring
- AI assistance: Artificial intelligence optimization of infusion parameters
- Data management: Seamless integration with electronic medical record systems
5.2 Material Science Advances
- Enhanced biocompatibility: Application of new biomaterials
- Functional enhancement: Antimicrobial, anticoagulant special functions
- Environmental sustainability: Biodegradable material development
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
As a fundamental medical device in clinical treatment, the safety and effectiveness of infusion sets directly relate to patient health and life. Medical institutions should:
- Establish standardized operating procedures to ensure all healthcare personnel master correct infusion set usage methods
- Improve quality management systems, implementing quality control throughout the procurement-to-use process
- Strengthen continuing education and training to enhance healthcare personnel’s professional skills and safety awareness
- Advance information management by utilizing modern technology to improve infusion therapy safety and efficiency
Through scientific and standardized use of infusion sets, patient safety can be maximized, treatment outcomes enhanced, and solid support provided for continuous improvement of clinical medical quality.
This guidance document is compiled based on current national standards and international best practices for reference by medical institutions and healthcare personnel. For the latest standard requirements or technical updates, please follow relevant official publications.