Global Supply Chain Strategies & Tariff Risk Management in 2025
This comprehensive guide addresses critical quality factors affecting medical syringes, medical needles, and blood collection needles, providing procurement professionals with actionable strategies to mitigate risks in an era of volatile trade tariffs. We analyze global supply chain advantages and present data-driven approaches for sourcing these essential medical devices.
1. Critical Quality Factors Affecting Medical Syringes, Medical Needles, and Blood Collection Needles
1.1 Raw Material Quality Standards
Medical-Grade Polymers for Medical Syringes
The foundation of quality medical syringes begins with premium raw materials:
- Polypropylene (PP): Primary material for syringe barrels and plungers, must meet USP Class VI or ISO 10993 biocompatibility standards
- Polyethylene (PE): Used in plunger seals, requiring non-toxic, pyrogen-free certification
- Medical-Grade Stainless Steel: Medical needles and blood collection needles typically utilize 304 or 316L stainless steel, directly impacting penetration performance and corrosion resistance
Critical Quality Metrics:
- Material purity with controlled additives
- Comprehensive biocompatibility testing documentation
- Supplier certifications (FDA Drug Master File, Certificate of Suitability to European Pharmacopoeia)
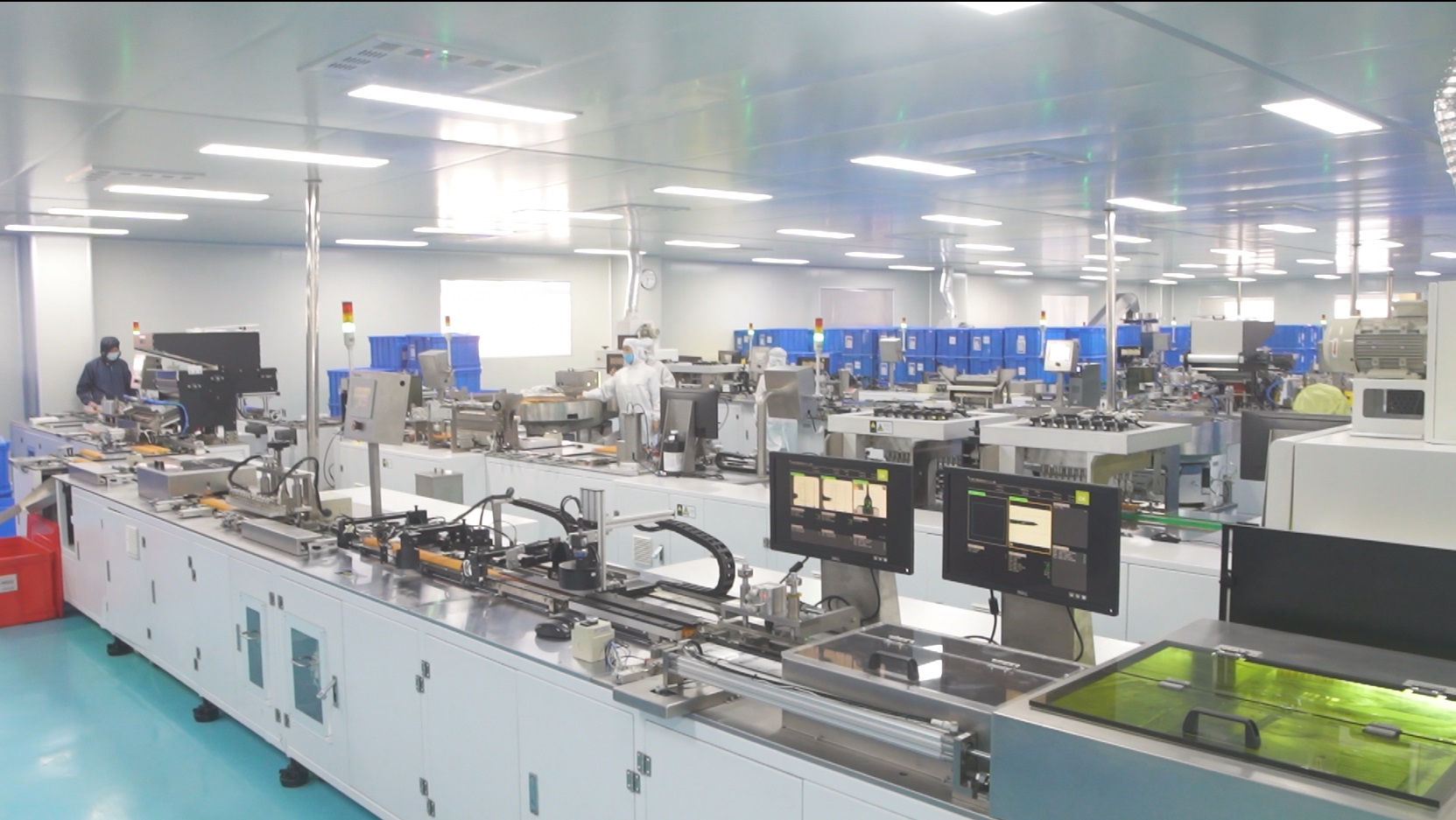
1.2 Manufacturing Process & Equipment Standards
Injection Molding for Medical Syringes
Precision manufacturing determines medical syringe quality:
- Mold Accuracy: Directly affects barrel-plunger fit and graduation precision
- Temperature/Pressure Control: Ensures consistency across production batches
- Cooling Time Management: Minimizes internal stress and dimensional variation
Needle Manufacturing Technology
Medical needle and blood collection needle production requires specialized processes:
- Tip Grinding Technology: Triple-bevel or five-bevel configurations reduce penetration pain
- Silicone Coating Application: Critical for smooth insertion and withdrawal
- Laser Cutting Precision: Ensures sharpness and consistency of needle tips
Sterilization Methods
All medical syringes, medical needles, and blood collection needles require validated sterilization:
- Ethylene Oxide (EO) Sterilization: Residual levels must remain <10ppm
- Gamma Irradiation: Dose control prevents material degradation
- Electron Beam Sterilization: Faster processing but higher cost investment
1.3 Cleanroom Environment & Quality Management
Cleanroom Classification Requirements
- Medical Syringe Assembly: ISO Class 7 (10,000 class) minimum
- Medical Needle Attachment: ISO Class 8 (100,000 class) or higher
- Environmental Monitoring: Temperature, humidity, particle count, microbial load
Quality Management Systems
Essential certifications for medical syringe, medical needle, and blood collection needle manufacturers:
- ISO 13485 Medical Device Quality Management System
- FDA 21 CFR Part 820 Quality System Regulation compliance
- EU MDR (Medical Device Regulation) conformity
1.4 Design Considerations
Ergonomic Design for Medical Syringes
- Graduation Accuracy: Typically ±5% tolerance per ISO 7886 standards
- Plunger Force Consistency: Smooth operation throughout injection cycle
- Connection Systems: Luer-lock or luer-slip compatibility with medical needles
Safety Features in Medical Needles
Modern medical needles and blood collection needles incorporate:
- Safety shield mechanisms for medical needles
- Anti-needlestick technology
- Blood flashback prevention in blood collection needles
- Retractable needle designs
1.5 Packaging & Storage Requirements
Packaging Integrity for Medical Syringes and Medical Needles
- Medical-grade blister or peel-pouch packaging
- Package integrity testing (dye penetration, bubble leak testing)
- Material compatibility studies
Storage Conditions
Proper storage preserves medical syringe, medical needle, and blood collection needle sterility:
- Temperature range: 5-30°C (41-86°F)
- Relative humidity: <80% RH
- Light protection requirements
- Shelf-life management (typically 3-5 years)

2. Risk Mitigation Strategies for Medical Syringe, Medical Needle, and Blood Collection Needle Procurement
2.1 Supplier Qualification & Certification Verification
Essential Documentation Checklist
Before sourcing medical syringes, medical needles, or blood collection needles, verify:
- ☑ ISO 13485 certification with current validity
- ☑ FDA registration (510(k) clearance or PMA approval)
- ☑ CE marking under EU MDR
- ☑ NMPA registration for Chinese market
- ☑ Target market-specific regulatory approvals

On-Site Audit Focus Areas
When evaluating medical syringe and medical needle manufacturers:
- Production facility cleanroom validation
- Quality control laboratory capabilities (equipment calibration, test method validation)
- Traceability systems and batch record management
- Adverse event reporting procedures
- Raw material supplier qualification processes
2.2 Contract Protection Mechanisms
Quality Assurance Clauses
Protect your medical syringe, medical needle, and blood collection needle procurement:
- Define technical specifications and acceptance criteria explicitly
- Establish sampling inspection protocols (AQL levels typically 1.5-2.5)
- Specify non-conformance handling procedures and liability allocation
- Include warranty periods and claim procedures
Supply Continuity Provisions
- Minimum order quantity (MOQ) and lead time commitments
- Safety stock obligations for critical products
- Supply disruption notification requirements
- Price adjustment mechanisms with frequency limitations
Intellectual Property Protection
- Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) for proprietary designs
- Exclusive distribution rights or territorial protection
- Non-compete clauses preventing sales to competitors
2.3 Quality Control Protocols
Incoming Inspection for Medical Syringes and Medical Needles

Implement rigorous testing for medical syringes, medical needles, and blood collection needles:
- Visual Inspection: Package integrity, labeling clarity
- Dimensional Verification: Needle gauge accuracy, syringe volume calibration
- Functional Testing: Plunger smoothness, needle sharpness
- Biological Evaluation: Sterility testing, pyrogen testing (when required)
Batch Traceability Systems
- Request Certificate of Analysis (CoA) for each batch
- Maintain comprehensive batch record database
- Implement First-In-First-Out (FIFO) inventory rotation
- Conduct periodic stability testing on stored products
Supplier Performance Metrics
Evaluate medical syringe and medical needle suppliers quarterly:
- On-Time-In-Full (OTIF) delivery rate
- First Pass Yield (quality conformance)
- Complaint response time and resolution effectiveness
- Annual supplier scorecard reviews
2.4 Multi-Source Procurement Strategy
Supplier Diversification
For medical syringes, medical needles, and blood collection needles:
- Primary supplier + backup supplier model (70/30 allocation recommended)
- Geographic distribution across different regions
- Avoid single-source dependency for critical components
Strategic Inventory Management
- Maintain 3-6 months safety stock for critical medical syringes and medical needles
- Calculate based on lead time, demand variability, and supply risk assessment
- Consider Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI) partnerships with key suppliers
2.5 Regulatory Compliance Management
Continuous Regulatory Monitoring
Stay informed about medical syringe, medical needle, and blood collection needle regulations:
- Subscribe to FDA, EMA, and other regulatory body notifications
- Participate in industry associations and regulatory seminars
- Engage regulatory consultants for periodic compliance reviews
Registration Maintenance
- Track registration certificate expiration dates
- Submit timely change notifications (materials, processes, manufacturing sites)
- Maintain current technical documentation files
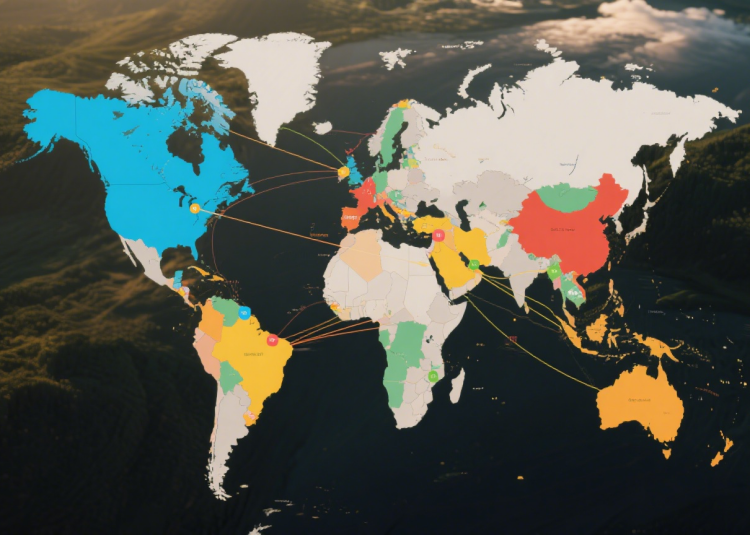
3. Global Supply Chain Analysis: Medical Syringes, Medical Needles, and Blood Collection Needles
3.1 Major Manufacturing Regions
CHINA: Global Leader in Medical Syringe and Medical Needle Production
Supply Chain Advantages for Medical Syringes:
China dominates global medical syringe production (60-70% of worldwide output):
- Complete Value Chain: Raw materials to finished medical syringes, medical needles, and blood collection needles
- Cost Leadership: Labor efficiency and economies of scale
- Massive Production Capacity: Rapid response to large-volume medical syringe orders
- Manufacturing Flexibility: Customization capabilities for specialized medical needles

Key Manufacturing Hubs:
- Jiangsu Province (Changzhou, Suzhou): Premium medical syringes and export-oriented medical needle manufacturers
- Zhejiang Province (Ningbo, Taizhou): Mid-range medical syringes with comprehensive supply chain support
- Shandong Province (Zibo): Raw material and chemical industry integration
Characteristics:
- Highly competitive pricing for medical syringes and medical needles
- Quality ranges from basic to world-class (leading brands: Kindly, Weigao, Kangkang)
- Rapid innovation capability for new medical syringe and medical needle designs
- Requires careful supplier selection and quality verification
EUROPE: Premium Medical Syringe and Medical Needle Technology
Supply Chain Advantages:
European medical syringe and medical needle manufacturers excel in:
- Technology Leadership: Advanced safety medical syringes and specialized medical needles
- Stringent Quality Standards: Full MDR and ISO compliance
- R&D Excellence: Innovation in blood collection needle systems and safety devices
- Brand Reputation: Trusted names in global healthcare
Major Players:
- Germany: B. Braun (precision medical syringes and medical needles)
- Ireland: BD European facilities (premium safety medical syringes)
- Spain: Pic Solution (disposable medical needles and blood collection needles)
Characteristics:
- Higher pricing for medical syringes and medical needles, but guaranteed quality consistency
- Ideal for markets requiring premium medical syringes and strict regulatory compliance
- Longer lead times require advance planning for medical needle procurement
- Strong environmental sustainability focus

UNITED STATES: Innovation in Medical Syringe and Medical Needle Design
Supply Chain Advantages:
American medical syringe and medical needle production features:
- FDA Compliance: Simplified approval for US market entry
- Technological Innovation: Safety-engineered medical needles, needleless systems
- Automation: High consistency in medical syringe manufacturing
- Domestic Priority: Emergency supply capabilities for medical syringes and medical needles
Leading Manufacturers:
- BD (Becton Dickinson): Global leader in medical syringes, medical needles, and blood collection needles
- Terumo Medical: Specialized blood collection needle systems
- Retractable Technologies: Safety medical syringe innovation
Characteristics:
- Primarily serves North American medical syringe and medical needle markets
- Highest price point justified by advanced technology
- Increasing offshore production (Mexico, Ireland) for cost optimization
INDIA: Emerging Medical Syringe and Medical Needle Manufacturing
Supply Chain Advantages:
India’s growing medical syringe and medical needle industry offers:
- Cost Competitiveness: Second only to China for medical syringe pricing
- Expanding Capacity: Government-supported medical device localization
- English Communication: Facilitates international medical needle procurement
- Pharmaceutical Infrastructure: Strong foundation for medical device production
Manufacturing Regions:
- Gujarat State: Medical device industrial parks
- Tamil Nadu: Export processing zones for medical syringes
Characteristics:
- Quality improving but generally below top-tier Chinese and Western medical syringe manufacturers
- Suitable for price-sensitive markets (Africa, South Asia)
- Supply chain reliability still developing
- Increasing GMP and ISO certification adoption
3.2 Comparative Supply Chain Analysis
| Region | Cost | Quality | Capacity | Lead Time | Innovation | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | High-volume medical syringe and medical needle procurement |
| Europe | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Premium medical syringes, strict regulatory markets |
| USA | ⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | US market medical needles and blood collection needles |
| India | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | Price-sensitive medical syringe markets |
4. Navigating Tariff Volatility: Strategic Approaches for Medical Syringe and Medical Needle Procurement
4.1 Tariff Impact Assessment Framework
Establish Monitoring Systems
For medical syringe, medical needle, and blood collection needle imports:
- Subscribe to customs authority notifications (US CBP, European Commission DG TAXUD)
- Utilize tariff databases (USITC, EU TARIC, WTO Tariff Database)
- Monitor trade policy developments (US-China relations, regional trade agreements)
Cost Calculation Models
Develop dynamic pricing tools for medical syringe and medical needle procurement:
- Include: Product cost + freight + insurance + tariffs + VAT + customs fees
- Scenario planning: Best case, baseline, worst case tariff situations
- Real-time calculation capabilities for rapid decision-making
4.2 Geographic Diversification Strategy
Multi-Region Sourcing for Medical Syringes and Medical Needles
Distribute medical syringe and medical needle procurement across trade zones:
Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) Members:
- China, Japan, South Korea, ASEAN nations
- Reduced tariffs on medical syringes and medical needles (HS 9018.31, 9018.32)
European Union:
- Single market advantages for medical syringe distribution
- MRA (Mutual Recognition Agreements) facilitate regulatory compliance
USMCA (United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement):
- Tariff-free movement of medical needles and blood collection needles
- Consider Mexican manufacturing for US market access
Other Preferential Trading Partners:
- Identify GSP (Generalized System of Preferences) eligible countries
- Leverage bilateral trade agreements for medical syringe imports
Dual-Source Implementation
For critical medical syringes, medical needles, and blood collection needles:
- Primary Supplier: Cost-optimized source (typically 70% of volume)
- Secondary Supplier: Tariff-hedged alternative in different customs territory (30%)
- Maintain active relationships with both to ensure switching capability
4.3 Free Trade Agreement Optimization
Rules of Origin Compliance
Maximize FTA benefits for medical syringe and medical needle imports:
- Verify suppliers can provide appropriate certificates of origin (Form A, Form E, RCEP CO)
- Understand product-specific rules (change in tariff classification, regional value content)
- Utilize cumulation provisions where applicable
RCEP Utilization for Medical Syringes
The RCEP agreement offers significant advantages for medical syringe and medical needle procurement:
- Progressive tariff elimination schedules for HS 9018 products
- Regional value content accumulation across member states
- Self-certification options reducing administrative burden
Other Preferential Programs
- GSP Programs: Duty-free treatment for medical syringes from developing countries to developed markets
- Bilateral Agreements: China-Switzerland, EU-Japan FTAs covering medical devices
4.4 HS Code Optimization & Customs Classification
Accurate Classification for Medical Syringes and Medical Needles
Proper tariff classification can significantly impact landed costs:
- Medical Syringes: Typically classified under HS 9018.31
- Medical Needles: Generally classified under HS 9018.32
- Blood Collection Needles: May fall under HS 9018.32 or 9018.90 depending on configuration
Classification Strategies
- Request Advance Rulings from customs authorities on proper classification
- Engage licensed customs brokers with medical device expertise
- Review classification annually as tariff schedules change
- Ensure consistency across all import jurisdictions
4.5 Supply Chain Finance & Currency Hedging
Foreign Exchange Risk Management
Protect medical syringe and medical needle procurement margins:
- Utilize forward contracts to lock exchange rates
- Diversify currency exposure (USD, EUR, CNY settlements)
- Negotiate currency terms in supplier agreements
Price Adjustment Mechanisms
Build flexibility into medical syringe and medical needle contracts:
- Include tariff adjustment clauses triggered by duty changes >5%
- Define clear calculation methodology and implementation timeline
- Share tariff risk between buyer and supplier through formulas
4.6 Bonded Warehousing & Free Trade Zones
Bonded Storage Strategy
Optimize cash flow for medical syringe and medical needle inventory:
- Store products in bonded warehouses to defer duty payment
- Clear customs in smaller batches aligned with sales cycles
- Particularly effective for high-volume medical syringe imports

Free Trade Zone (FTZ) Advantages
Leverage FTZ benefits for medical needle and blood collection needle distribution:
- Major zones: Shanghai FTZ, Shenzhen Qianhai, Singapore, Dubai
- Duty deferral, manufacturing operations, value-added services
- Consider establishing regional distribution hubs in FTZs
Cross-Border E-Commerce Models
Alternative channels for smaller-volume medical syringe procurement:
- Utilize cross-border e-commerce pilot zones
- Simplified customs procedures for qualified transactions
- Potentially lower duty rates under e-commerce programs
4.7 Localization & Near-Shoring Considerations
Long-Term Strategic Options
For major medical syringe and medical needle markets:
- Local Manufacturing: Evaluate establishing production in high-tariff destinations
- Assembly Operations: Import components, final assembly in-market
- Technology Transfer: License manufacturing to local partners
Partnership Models
Reduce tariff exposure on medical syringes and medical needles:
- Joint ventures with regional manufacturers
- OEM/ODM arrangements transferring production capacity
- Maintain core technology control while diversifying geographic footprint
4.8 Regulatory & Compliance Preparedness
Trade Compliance Audits
Ensure medical syringe and medical needle imports meet all requirements:
- Verify compliance with import/export control regulations
- Understand anti-dumping and countervailing duty risks
- Avoid transactions with sanctioned entities or countries
Legal Resources
Prepare for trade disputes affecting medical syringes and medical needles:
- Establish relationships with international trade attorneys
- Maintain documentation for trade remedy investigations
- Participate in industry associations for collective advocacy
4.9 Dynamic Decision Framework
Tariff Response Matrix for Medical Syringe Procurement
Implement graduated responses based on duty increases:
Tariff Increase <5%:
- Absorb cost or implement minor price adjustments
- Continue with primary medical syringe supplier
Tariff Increase 5-15%:
- Activate secondary suppliers in alternative customs territories
- Shift 20-30% of medical needle volume
- Renegotiate pricing with existing suppliers
Tariff Increase 15-25%:
- Major reallocation of medical syringe sourcing
- Accelerate qualification of new medical needle suppliers
- Restructure contracts with tariff adjustment clauses
Tariff Increase >25%:
- Consider localization options for medical syringes
- Evaluate alternative market strategies
- Long-term supply chain reconfiguration
Contract Flexibility
Design agreements that adapt to tariff changes:
- Shorter contract terms (6-12 months) rather than multi-year commitments
- Include early termination or modification clauses
- Phased volume commitments maintaining decision flexibility
4.10 Industry Collaboration & Intelligence Sharing
Trade Association Engagement
Participate in organizations focused on medical syringes and medical needles:
- Advanced Medical Technology Association (AdvaMed)
- European Medical Device Industry Association (Eucomed)
- China Chamber of Commerce for Import and Export of Medicines & Health Products (CCCMHPIE)
Government Liaison
Advocate for favorable treatment of medical syringe and medical needle imports:
- Submit comments during public consultation periods
- Participate in trade policy hearings
- Request temporary duty suspensions or exclusions for critical medical devices
5. Action Plan: Implementing Your Medical Syringe and Medical Needle Procurement Strategy
Phase 1: Immediate Actions (0-6 Months)
Priority 1: Tariff Impact Assessment
- Calculate current duty burden on medical syringe, medical needle, and blood collection needle imports
- Identify highest-risk products and markets
- Develop cost models incorporating various tariff scenarios
Priority 2: Supplier Communication
- Engage current medical syringe and medical needle suppliers on tariff-sharing mechanisms
- Request certifications of origin and FTA documentation
- Discuss dual-sourcing possibilities
Priority 3: Backup Supplier Identification
- Qualify 2-3 alternative medical syringe manufacturers in different customs territories
- Conduct preliminary audits of medical needle suppliers in low-tariff regions
- Test small orders to validate quality and delivery performance
Priority 4: Contract Review
- Audit existing agreements for tariff provisions
- Add adjustment clauses to new medical syringe and medical needle contracts
- Ensure flexibility for source-of-supply changes
Phase 2: Medium-Term Initiatives (6-18 Months)
Strategic Diversification
- Implement multi-region sourcing for critical medical syringes and medical needles
- Achieve at least 70/30 split between primary and secondary suppliers
- Establish relationships in RCEP member countries
FTA Optimization
- Ensure all eligible medical syringe and medical needle shipments utilize preferential treatment
- Train procurement team on rules of origin and documentation requirements
- Conduct supplier training on certificate of origin preparation
Inventory & Logistics Optimization
- Establish strategic stock of medical syringes and medical needles (3-6 months)
- Implement bonded warehousing for major import markets
- Optimize order frequency and quantities for tariff efficiency
Quality System Alignment
- Complete comprehensive audits of new medical needle suppliers
- Ensure all sources meet ISO 13485 and regulatory requirements
- Implement unified quality standards across supply base
Phase 3: Long-Term Transformation (18+ Months)
Supply Chain Reconfiguration
- Restructure global medical syringe and medical needle sourcing network based on total landed cost
- Consider regional manufacturing hubs for key markets
- Develop strategic partnerships with leading suppliers
Localization Feasibility Studies
- Evaluate establishing medical syringe production in major consumption markets
- Analyze make-vs-buy economics including tariff savings
- Consider joint venture or licensing models
Innovation Partnerships
- Collaborate with medical needle suppliers on new safety-engineered products
- Co-develop next-generation blood collection needle systems
- Share intellectual property for mutual benefit
Digital Transformation
- Implement supply chain visibility platform for real-time tracking
- Deploy predictive analytics for demand forecasting
- Automate tariff monitoring and cost calculations
6. Key Performance Indicators for Medical Syringe and Medical Needle Procurement
Track these metrics to ensure procurement success:
Cost Metrics
- Total landed cost per unit (medical syringe, medical needle, blood collection needle)
- Tariff cost as percentage of total procurement spend
- Cost savings from FTA utilization
- Currency hedging effectiveness
Quality Metrics
- Incoming inspection pass rate for medical syringes and medical needles
- Customer complaint rate per million units
- Regulatory compliance rate (zero defects target)
- Supplier quality audit scores
Supply Continuity Metrics
- On-time-in-full delivery rate
- Supply disruption incidents (target: zero)
- Inventory days on hand
- Supplier diversification index (target: >2 qualified sources per product)
Compliance Metrics
- Percentage of imports utilizing FTA preferences
- Customs classification accuracy rate
- Regulatory inspection pass rate
- Certificate of origin accuracy
Conclusion: Securing Your Medical Syringe and Medical Needle Supply Chain
In an era of unprecedented trade policy volatility, successful procurement of medical syringes, medical needles, and blood collection needles requires a sophisticated, multi-faceted approach combining quality assurance, regulatory compliance, and strategic tariff management.
Key Takeaways:
- Quality First: Never compromise medical syringe and medical needle quality for cost savings—patient safety and regulatory compliance must remain paramount
- Diversification is Essential: Build a resilient supply network with multiple qualified sources for medical syringes and medical needles across different geographic regions
- Leverage Trade Agreements: Actively utilize RCEP, FTAs, and preferential programs to minimize tariff impact on medical syringe and medical needle imports
- Maintain Flexibility: Structure contracts and relationships to enable rapid adaptation to changing tariff landscapes
- Strategic Partnerships: Develop long-term collaborative relationships with key medical syringe and medical needle suppliers built on mutual trust and shared success
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement systems for real-time tracking of tariff changes, regulatory updates, and supply chain disruptions
The Path Forward:
The global market for medical syringes, medical needles, and blood collection needles will continue evolving. Successful procurement organizations will be those that:
- Invest in robust supplier qualification and quality systems
- Maintain geographic and supplier diversity
- Stay informed about trade policy developments
- Build flexible contracts and relationships
- Focus on total value, not just initial purchase price
By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, you can secure a reliable, compliant, cost-effective supply of medical syringes, medical needles, and blood collection needles that meets your organization’s needs while navigating the complexities of international trade.
Remember: The goal is not simply to minimize costs, but to optimize total value while ensuring uninterrupted supply of critical medical devices that healthcare providers depend on to deliver safe, effective patient care.
Additional Resources
Regulatory Agencies:
- FDA Medical Devices: www.fda.gov/medical-devices
- European Medicines Agency: www.ema.europa.eu
- China NMPA: www.nmpa.gov.cn
Trade Information:
- World Trade Organization: www.wto.org
- USITC DataWeb: dataweb.usitc.gov
- EU TARIC Database: ec.europa.eu/taxation_customs/dds2/taric
Industry Associations:
- AdvaMed: www.advamed.org
- MDMA (Medical Device Manufacturers Association): www.medicaldevices.org
- CCCMHPIE: www.cccmhpie.org.cn
This guide is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, regulatory, or professional advice. Consult with qualified experts regarding specific procurement decisions, regulatory compliance, and trade matters affecting medical syringes, medical needles, and blood collection needles.