As a seasoned healthcare professional, I frequently encounter colleagues and patients’ families with questions about disposable infusion sets, IV infusion sets, and infusion equipment. Today, I’ll explain every detail of medical infusion sets in the most accessible way possible, helping you thoroughly understand this seemingly simple yet critically important medical device.
What is an Infusion Set: Understanding from Ground Zero
Basic Concept Analysis
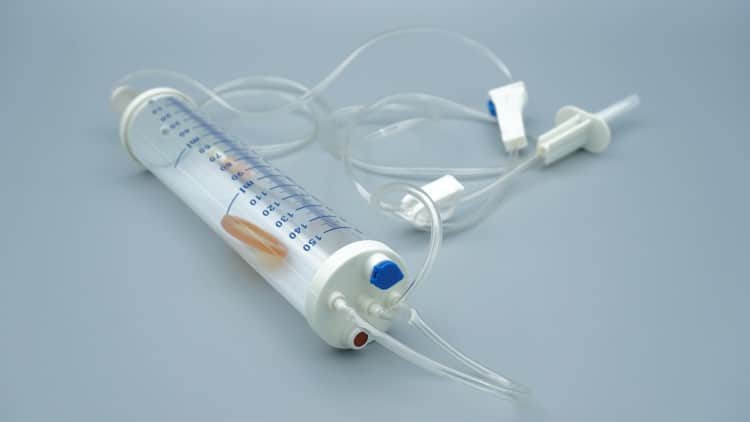
An infusion set (also called IV infusion set or drip set) is one of the most common disposable medical devices in hospitals. Simply put, it’s like a “liquid transport pipeline system” that safely and accurately delivers medications from IV bags to patients’ blood vessels.
Why do we need infusion sets? Imagine if we had to use syringes to inject medications directly – we could only inject small amounts at a time and would need repeated injections, which would be both painful and dangerous for patients. Infusion sets solve this problem by enabling:
- Continuous, stable medication delivery without repeated punctures
- Precise control of medication delivery rate to prevent too-rapid drug entry
- Reduced healthcare worker workload
- Lower infection risk
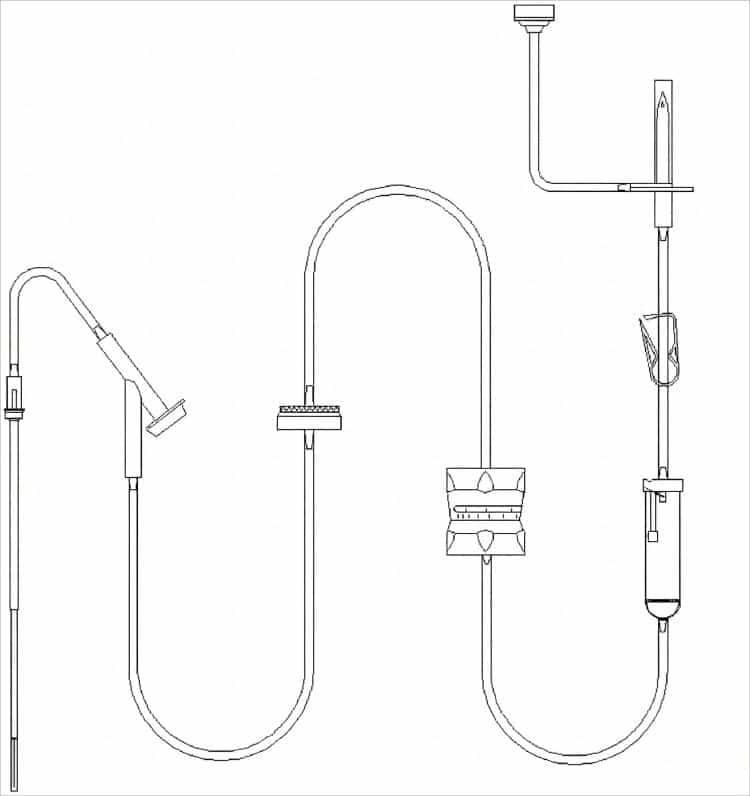
Detailed Component Analysis of Infusion Sets
Let me explain the working principles of each component in detail:
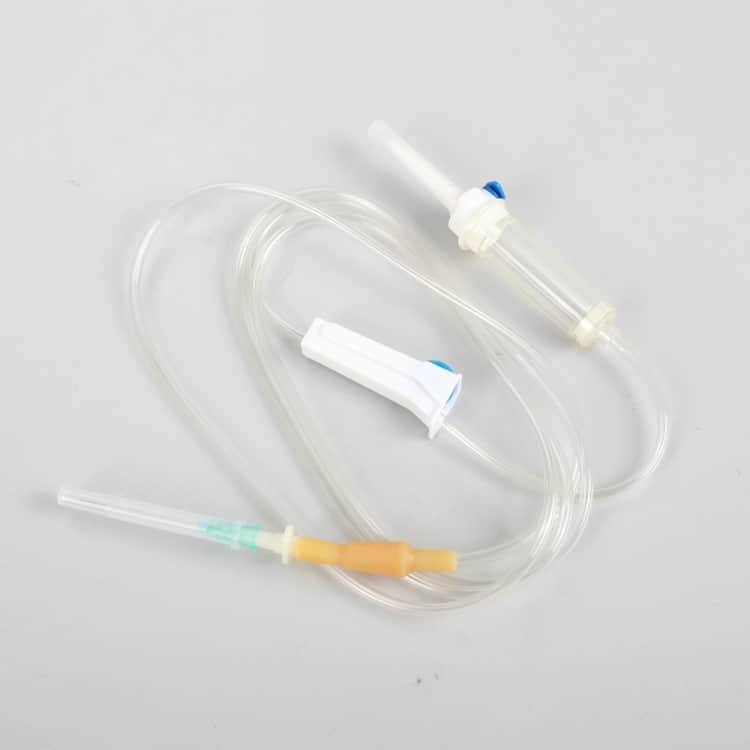
1. Piercing Spike (Insertion Needle)
- Function: Pierces the rubber stopper of IV bags to establish fluid pathway
- Why designed this way: Rubber stoppers are self-sealing – they won’t leak after needle removal
- Material requirements: Must be medical-grade stainless steel to ensure sharpness and sterility
2. Drip Chamber (Drop Chamber)
- Function: This is the “heart” of the infusion set, controlling fluid flow drop by drop
- Working principle: Uses surface tension – fluid forms drops at the chamber outlet before falling
- Why drop formation: Makes it easy to calculate infusion rate (typically 20 drops = 1mL)
- Volume design: Usually 15-20mL capacity, with fluid level maintained at 1/3 height
3. Tubing (IV Tubing)
- Material: Medical-grade PVC or silicone, must be transparent and non-toxic
- Length: Typically 150-200cm – long enough for convenient operation but not so long as to increase resistance
- Inner diameter: 2-3mm, ensuring adequate flow rate while preventing blockage
4. Flow Regulator (Flow Control Clamp)
- Structural types: Roller clamp or pinch clamp
- Working principle: Controls flow rate by compressing tubing to change lumen size
- Precision: Quality regulators enable stepless speed control
5. Needle Connection Port
- Standard interface: Luer connector, international universal standard
- Material requirements: Medical-grade plastic ensuring airtight seal
In-Depth Analysis of Infusion Set Working Principles
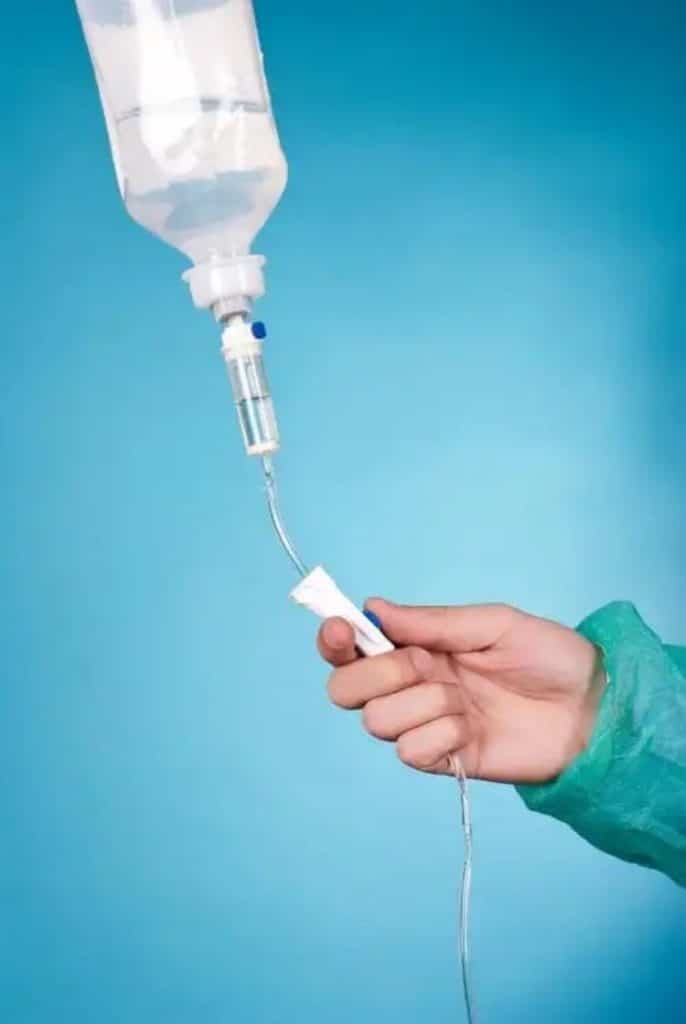
Gravity Infusion Principles
Basic physics principle: Infusion sets operate using gravity and atmospheric pressure differential
Detailed working process:
- Establishing fluid column: IV bag is hung high (typically 60-100cm above patient’s heart level)
- Pressure calculation: Every 10cm elevation increases pressure by approximately 1mmHg
- Flow rate formula: Flow rate = √(2gh), where g is gravitational acceleration, h is height difference
- Practical application: This is why IV poles must have sufficient height – too low and fluid won’t flow
Why does fluid continue flowing? Many wonder: IV bags are sealed, so wouldn’t fluid outflow create a vacuum?
The answer lies in the clever piercing spike design:
- The piercing spike actually has a dual-lumen structure
- One lumen allows fluid outflow
- The other lumen allows air to enter the bag
- This maintains atmospheric pressure inside the bag, enabling continuous fluid flow
Drop Rate Control Principles
Why control drop rate?
- Drug safety: Certain medications (like potassium salts) can be life-threatening if infused too rapidly
- Cardiac burden: Rapid infusion increases cardiac workload, especially in elderly patients
- Therapeutic considerations: Some drugs need slow release for optimal effectiveness
Drop rate calculation method: Standard formula: Drop rate (drops/min) = Total infusion volume (mL) × Drop factor ÷ Infusion time (minutes)
Example: 500mL normal saline over 4 hours, drop factor 20 drops/mL Drop rate = 500 × 20 ÷ 240 = 41.7 drops/minute
Core Functions of Infusion Sets Explained
1. Precision Drug Delivery System
Multiple safety safeguards:
- Filtration function: Built-in 15-micron filter removes particles and bacteria
- Unidirectional flow: Prevents blood backflow, avoiding infection
- Closed system: Complete sterile pathway from drug vial to blood vessel
Why is filtration necessary? Even the cleanest drug solutions may develop microscopic particles during preparation and storage. These particles entering blood vessels could cause:
- Capillary blockage
- Local tissue necrosis
- Allergic reactions
- Thrombus formation
2. Intelligent Flow Rate Control System
Multi-level flow rate control:
- Coarse adjustment: By adjusting IV bag height
- Fine adjustment: Through flow regulator
- Micro adjustment: By observing drip chamber drop rate
Importance of flow rate monitoring: Different drugs have different safe infusion rates:
- Normal saline: Can be relatively fast, 40-60 drops/minute
- Concentrated electrolytes: Must be slow, 10-20 drops/minute
- Chemotherapy drugs: Strictly per physician orders, usually very slow
- Blood products: Start slowly, increase appropriately if no adverse reactions
3. Real-time Monitoring and Alert System
Visual monitoring:
- Drip chamber observation: Drop size, frequency, color
- Tubing inspection: Check for air bubbles, precipitates, blockages
- Connection monitoring: Ensure secure connections, no leakage
Scientific Basis for Usage Precautions
Biological Foundation of Sterile Technique
Why strict sterility? IV infusion enters blood circulation directly, bypassing the body’s natural defense barriers:
- Skin barrier: Normally bacteria cannot directly enter bloodstream
- Immune system: Bloodstream infections are harder to control than local infections
- Systemic spread: Once bacteria enter blood, they rapidly spread throughout the body
Key points of sterile technique:
- Hand disinfection: Use alcohol-based hand sanitizer for at least 20 seconds
- Operating environment: Keep work surfaces clean, avoid contaminated areas
- Equipment sterilization: All equipment contacting drug solutions must be sterile
- Time control: Opened infusion sets should be used within 4 hours
Anatomical Considerations for Venipuncture
Optimal puncture site selection:
Upper extremity preferred sites:
- Cephalic vein: Fixed position, doesn’t slide easily
- Dorsal hand venous network: Suitable for short-term infusion
- Median cubital vein: Large but prone to dislodgement during movement
Physics principles of puncture angle:
- Insertion angle: 15-30 degrees; too steep may penetrate vessel
- Insertion depth: Advance 2-3mm after blood return
- Securing method: Use medical tape in “井” (well) pattern for fixation
Physiological Basis of Infusion Rate
Human circulatory system capacity:
Adult standards:
- Normal adults: Heart pumps 5-6 liters per minute
- Safe infusion rate: Generally not exceeding 500mL per hour
- Special situations: Shock patients may require rapid fluid resuscitation
Pediatric special considerations:
- Small blood volume: Newborn blood volume only 80-90mL/kg
- Cardiac function: Children have limited cardiac compensatory ability
- Calculation formula: Pediatric infusion rate = Weight (kg) × Hourly maintenance volume (mL/kg)
Elderly physiological characteristics:
- Decreased cardiac function: Ejection fraction may be reduced
- Poor vascular elasticity: Prone to infiltration
- Reduced renal function: Decreased fluid excretion capacity
In-Depth Answers to Common Questions
Why does fluid infiltration occur?
Infiltration mechanisms:
- Needle displacement: Patient movement causes needle tip to leave vascular lumen
- Vascular spasm: Cold or irritation causes vessel constriction
- Venous pressure: Infusion pressure exceeds venous pressure
- Vascular injury: Vessel wall damage during puncture
Scientific basis for prevention measures:
- Appropriate fixation: Secure but not restricting blood circulation
- Regular checks: Inspect every 30 minutes for early abnormality detection
- Patient education: Inform patients to keep puncture limb relatively immobile
Why regularly change infusion sites?
Vascular endothelial repair mechanisms:
- Inflammatory response: Foreign body irritation causes local inflammation
- Endothelial damage: Prolonged irritation damages endothelial cells
- Repair time: Generally requires 72 hours for basic repair completion
- Infection risk: Longer duration increases bacterial colonization risk
Technical Specifications and Quality Standards for Infusion Sets
International Standards and Certifications
ISO standard requirements:
- ISO 8536-4: Standard for disposable IV infusion sets
- Biocompatibility: ISO 10993 series standards
- Sterility assurance level: SAL 10⁻⁶ (one in a million probability of viable organisms)
Quality control indicators:
- Drop factor accuracy: Within ±10%
- Flow rate accuracy: <±5% error under specified pressure
- Filtration efficiency: >99% efficiency for 15-micron particles
- Connection strength: >15N for all interface connections
Materials Science and Safety
Reasons for PVC material selection:
- High transparency: Facilitates drug solution observation
- Chemical stability: No reaction with most drugs
- Good flexibility: Not easily broken, convenient operation
- Moderate cost: Suitable for single use
DEHP plasticizer concerns:
- Function: Increases PVC flexibility
- Controversy: Potential endocrine disruption effects
- Solutions: Use DEHP-free formulations or alternative materials
Technical Points for Special Application Scenarios
Chemotherapy Drug Infusion
Special requirements:
- Material compatibility: Some chemotherapy drugs corrode standard PVC
- Light protection: Some drugs require light-protected infusion sets
- Precise control: Usually requires infusion pump assistance
Blood Product Transfusion
Specialized blood infusion sets:
- Filter specifications: 170-200 microns to filter blood clots
- Material selection: Special materials to prevent hemolysis
- Transfusion rate: Strict speed gradient management
Pediatric-Specific Infusion Sets
Design features:
- Micro-drop: 60 drops/mL (adult sets: 20 drops/mL)
- Smaller volume: Reduces drug waste
- Safety design: Prevents operational errors
Future Development Trends and Technological Innovation
Smart Infusion Sets
IoT integration:
- Flow rate monitoring: Real-time monitoring and data upload
- Abnormality alerts: Automatic detection of blockages, infiltration, etc.
- Remote management: Centralized monitoring at nursing stations
Environmental Protection and Sustainability
Material innovation:
- Biodegradable materials: Reduce medical waste burden
- Recycling: Component recycling technologies
- Packaging optimization: Reduce packaging material usage
Personalized Customization
Precision medicine needs:
- Patient-specific: Customized infusion sets based on patient characteristics
- Drug compatibility: Specialized infusion sets for specific medications
- Smart algorithms: AI-assisted infusion protocol optimization
Procurement and Selection Guide
Hospital Procurement Considerations
Quality indicator assessment:
- Basic quality: Compliance with national and industry standards
- Clinical applicability: Meeting various department usage requirements
- Safety performance: Adverse event incidence statistics
- Cost-effectiveness: Comprehensive consideration of price and effectiveness
Supplier evaluation criteria:
- Production qualifications: Appropriate manufacturing licenses
- Quality systems: ISO 13485 quality management system certification
- Technical support: Professional technical training and support
- Supply stability: Long-term stable supply capability
Differentiated Needs by Department
Internal medicine wards:
- Standard type: Suitable for most drug infusions
- Precision filtration type: Suitable for antibiotics and other drugs
Surgical wards:
- High-flow type: Suitable for post-operative rapid fluid replacement
- Multi-channel type: Simultaneous infusion of multiple drugs
Pediatric wards:
- Micro-volume type: Precise control of small-dose administration
- Safety type: Child-tamper-resistant design
ICU critical care:
- High-precision type: For use with infusion pumps
- Multi-functional type: Integrated pressure monitoring features
Conclusion
Infusion sets, as indispensable medical devices in modern healthcare, involve knowledge from multiple disciplines in their design and use. From materials science to biomedical engineering, from fluid mechanics to human physiology, every detail relates to patient safety.
As healthcare professionals, we must not only master correct operational skills but also understand the underlying scientific principles. Only this way can we make correct judgments in clinical practice and provide the safest, most effective treatment for patients.
For hospital administrators and procurement personnel, selecting appropriate infusion set products is equally important. Quality disposable infusion sets not only ensure treatment effectiveness but also reduce medical risks and improve work efficiency.
About Our Professional Services
As a professional infusion set manufacturer and supplier, we understand the importance of every detail for patient safety. Our products are manufactured strictly according to international standards, covering a complete range of IV infusion sets, precision filtration infusion sets, pediatric-specific infusion sets, and other medical infusion set products.
Our Advantages:
✅ Quality Assurance: ISO 13485 certified, compliant with FDA and CE standards
✅ Technical Innovation: Continuous R&D investment, leading industry technological development
✅ Professional Service: Comprehensive services from product selection to technical training
✅ Stable Supply: Established complete production and logistics systems ensuring timely delivery
Product Portfolio:
- Standard Disposable Infusion Sets
- Precision Filtration IV Sets
- Pediatric Micro-Drop Infusion Sets
- Blood Transfusion Sets
- Chemotherapy-Compatible Infusion Sets
- Custom OEM/ODM Solutions
If you have any requirements or questions about our infusion set products, please contact our professional team. We are committed to contributing our expertise to every patient’s safety and well-being.
Contact us today for professional medical device solutions that meet your healthcare facility’s specific needs.