In modern clinical diagnostics, the accuracy of test results begins long before samples reach the analyzer. Blood collection tubes serve as the critical first step in specimen management, with the global market for these essential medical devices projected to reach $4.2 billion by 2027. Understanding the different tubes for blood collection and their specific applications is fundamental for healthcare professionals, laboratory managers, and procurement specialists seeking to optimize diagnostic accuracy and operational efficiency.

Understanding Blood Collection Tubes: Foundation of Diagnostic Testing
Blood collection tubes are evacuated, sterile containers designed to collect, transport, and preserve blood specimens for laboratory analysis. These tubes maintain precise vacuum levels—typically ranging from -0.08 to -0.10 MPa—ensuring consistent blood draw volumes and proper additive-to-blood ratios. Modern vacuum blood collection systems have revolutionized phlebotomy practices since their introduction in the 1940s, reducing contamination risks by 73% compared to open collection methods.
The functionality of these tubes extends beyond simple containment. Each tube type contains specific additives that interact with blood components to preserve specimen integrity for particular test categories. The interior walls feature specialized coatings applied through precise manufacturing processes, ensuring uniform distribution and optimal performance.
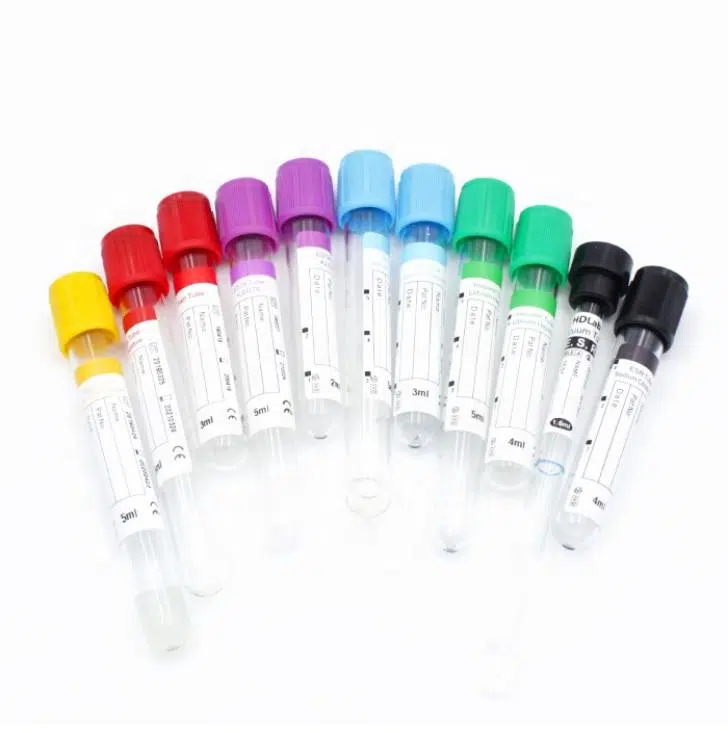
Types of Blood Collection Tubes: A Comprehensive Classification
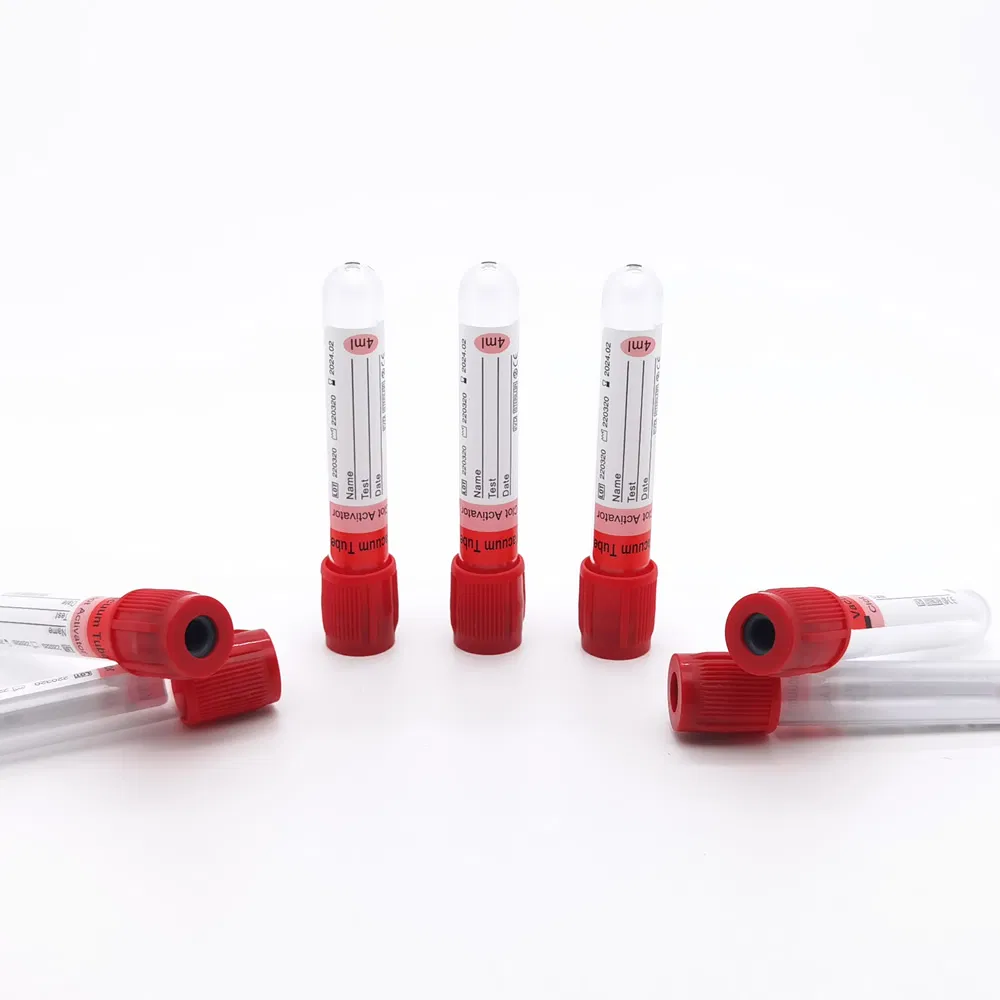
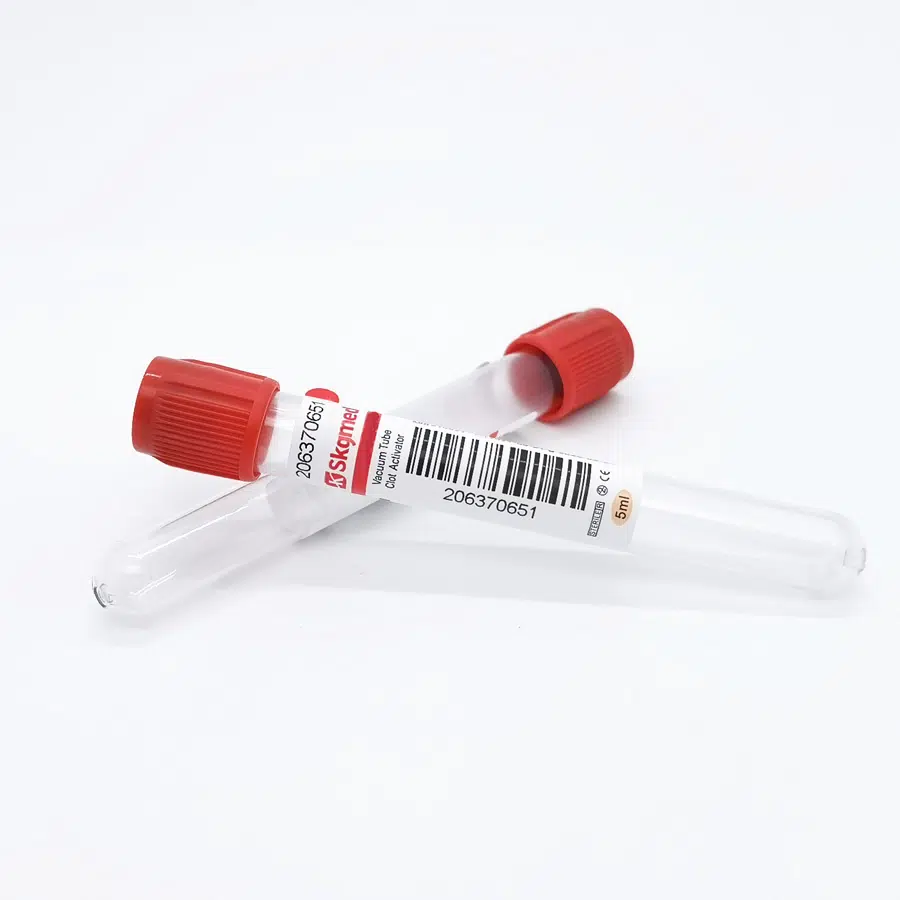
1. Clot Activator Tubes (Red/Orange Cap)
The pro-coagulation tube, also known as the clot activator tube, represents one of the most commonly used types of blood collection tubes in clinical settings. These tubes contain silica particles or glass beads that activate the coagulation cascade, accelerating clot formation from the typical 30-60 minutes down to 5-15 minutes.
Technical specifications:
- Coagulation time: 5-15 minutes at room temperature (20-25°C)
- Centrifugation requirements: 3,000-4,000 rpm for 10 minutes
- Serum yield: Approximately 45-50% of collected blood volume
- Shelf life: 24 months for glass tubes, 18 months for PET tubes
The controlled coagulation process prevents hemolysis—a critical concern that affects up to 3.3% of emergency department samples and can compromise test results for potassium, lactate dehydrogenase, and other analytes.
2. Serum Separator Tubes (Yellow Cap)
These advanced tubes combine clot activators with thixotropic gel barriers. During centrifugation, the gel migrates to form a stable partition between serum and cellular components, maintaining specimen stability for 48-72 hours at refrigerated temperatures.
3. EDTA Tubes (Purple Cap)
Containing ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (K2 or K3 formulation), these tubes chelate calcium ions to prevent coagulation. EDTA tubes are essential for hematology applications, preserving cell morphology for complete blood counts and blood typing procedures.
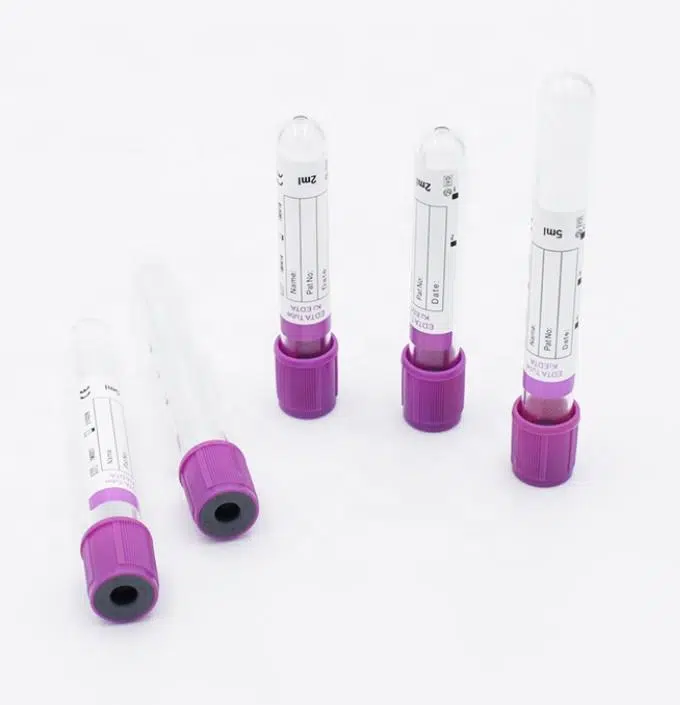

4. Citrate Tubes (Blue/Black Cap)
Available in 3.2% (1:9 ratio) and 3.8% (1:4 ratio) concentrations, citrate tubes are specifically designed for coagulation studies. The precise citrate-to-blood ratio is critical—even 10% deviation can alter prothrombin time results by 8-12%.
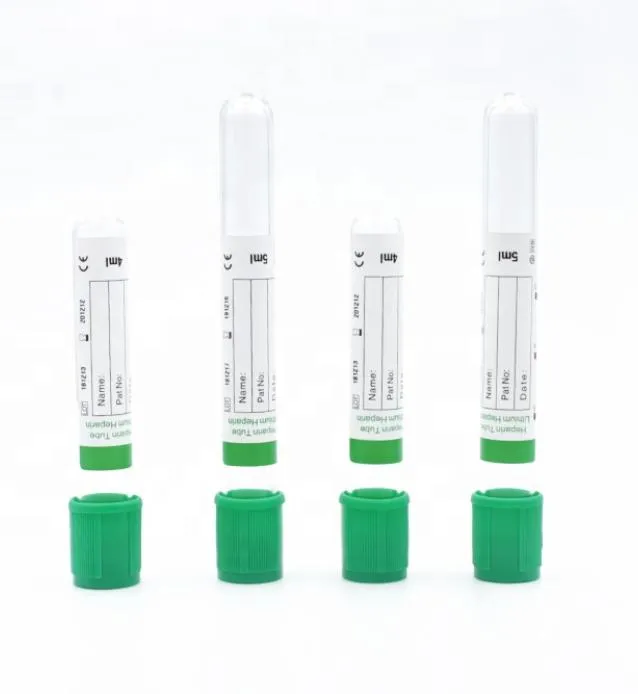
5. Heparin Tubes (Green Cap)
Lithium or sodium heparin prevents coagulation by inhibiting thrombin formation. These tubes provide plasma samples for chemistry panels, with results available 15-20 minutes faster than serum-based methods.

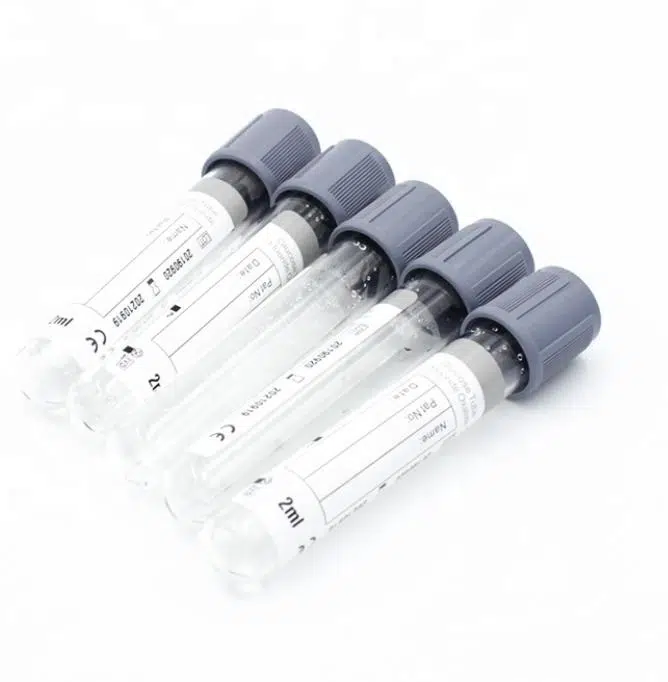
6. Glucose Tubes (Grey Cap)
Containing sodium fluoride and potassium oxalate, these tubes inhibit glycolysis, preserving glucose concentrations for up to 72 hours—essential for diabetes diagnosis and monitoring.

Blood Collection Tubes and Tests: Matching Tubes to Clinical Applications
Understanding the relationship between blood collection tubes and tests is crucial for diagnostic accuracy. Selecting the wrong tube type can lead to specimen rejection rates as high as 2.1% in some facilities, causing delays and requiring patient recollection.
Biochemistry Testing Applications
For routine chemistry panels including liver function, kidney function, and electrolyte analysis, clot activator tubes with 5ml capacity offer optimal performance. The rapid coagulation time—typically completing within 10 minutes—enables faster turnaround times in high-volume laboratories processing 500+ specimens daily.
Key biochemistry applications:
- Liver enzymes (ALT, AST, ALP, GGT)
- Renal function markers (creatinine, BUN, uric acid)
- Lipid profiles (cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL, LDL)
- Electrolyte panels (sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium)
- Cardiac markers (troponin, CK-MB, BNP)

Immunology and Serology Testing
Clot activator tubes provide clean serum samples free from anticoagulant interference, making them ideal for antibody detection, infectious disease screening, and immunoassay procedures. Studies demonstrate that proper tube selection reduces false-positive rates in immunoassays by up to 15%.
Hematology Applications
Purple-cap EDTA tubes preserve cellular elements for 24 hours when refrigerated, supporting complete blood counts, differential analysis, and blood typing. The K2 EDTA formulation, spray-dried onto tube walls at concentrations of 1.5-2.2 mg per ml of blood, ensures consistent anticoagulation.
Coagulation Studies
Blue-cap citrate tubes maintain the delicate balance required for PT/INR, aPTT, and D-dimer testing. Fill level accuracy is critical—tubes must be filled to within 90-110% of stated volume to maintain proper citrate dilution.
Different Tubes for Blood Collection: Size and Material Considerations
The physical characteristics of different tubes for blood collection significantly impact clinical utility and procurement decisions.
Size Specifications
Blood collection tubes are manufactured in standardized dimensions:
Common sizes (diameter x length in mm):
- 12×75: Pediatric applications, 2-3ml capacity
- 12×100: Standard draws, 3-4ml capacity
- 13×75: Standard adult use, 4-5ml capacity
- 13×100: Larger volume needs, 5-6ml capacity
- 16×100: High-volume testing, 8-10ml capacity
The 5ml tube size (typically 13×75 or 13×100) represents the most versatile option, providing sufficient specimen volume for multiple test parameters while minimizing patient blood loss—a critical consideration given that hospitalized patients may lose 40-70ml daily through diagnostic phlebotomy.

Material Selection: PET vs. Glass
Glass tubes:
- Superior chemical inertness
- Excellent optical clarity for visual inspection
- 24-month shelf life
- Higher breakage risk (2-3% in typical laboratory settings)
- Traditional choice for specialized coagulation testing
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) tubes:
- 99.8% shatter-resistance rating
- 18-month shelf life
- 15-20% lighter weight, reducing shipping costs
- Reduced biohazard exposure risk
- Increasingly preferred in high-volume settings
Material selection impacts procurement budgets significantly. While PET tubes cost 8-12% more per unit, reduced breakage and disposal costs often result in 5-7% total cost savings over 12-month periods.

Quality Standards and Certification Requirements
Medical device regulations mandate strict quality controls for blood collection tubes. ISO 13485:2016 certification ensures manufacturing quality management systems meet international standards, while CE marking confirms compliance with European Union medical device regulations.
Critical quality parameters:
- Vacuum stability: Must maintain ≥90% initial vacuum for entire shelf life
- Additive precision: ±5% tolerance on stated concentrations
- Sterility assurance level: 10⁻⁶ (one non-sterile unit per million)
- Heavy metal limits: Lead <0.5 ppm, cadmium <0.1 ppm
- EO (ethylene oxide) sterilization residuals: <250 ppm total
Procurement Considerations for Healthcare Facilities
Laboratory managers and procurement specialists evaluating blood collection tube suppliers should assess multiple factors beyond unit pricing.
Volume-Based Requirements
A 200-bed hospital typically consumes 150,000-200,000 blood collection tubes annually. High-volume facilities benefit from direct factory supply arrangements, potentially reducing costs by 15-25% compared to distributor pricing while ensuring supply chain stability.
Tube Type Distribution
Typical hospital laboratory tube usage patterns:
- Clot activator tubes: 35-40%
- EDTA tubes: 25-30%
- Citrate tubes: 8-12%
- Heparin tubes: 10-15%
- Specialized tubes: 8-10%
Inventory Management
Just-in-time inventory systems balanced against tube shelf life optimize working capital. For PET tubes with 18-month shelf life, maintaining 3-4 months inventory provides adequate buffer while minimizing expiration waste, which averages 1.2-1.8% in well-managed facilities.
Best Practices for Blood Collection Tube Selection and Use
Order of Draw Protocol
Proper collection sequence prevents cross-contamination between tube additives. The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) recommends:
- Blood culture tubes (sterile collections)
- Citrate tubes (coagulation)
- Serum tubes (clot activator)
- Heparin tubes (plasma)
- EDTA tubes (whole blood)
- Glycolysis inhibitor tubes (glucose)
Adherence to this protocol reduces additive carryover errors by 94%.
Storage and Handling
Proper storage maintains tube integrity:
- Temperature: 4-25°C (39-77°F)
- Humidity: <80% relative humidity
- Position: Upright storage prevents cap-additive contact
- Light protection: Minimize UV exposure for photosensitive additives
Sample Processing Timeline
Time-to-centrifugation impacts result accuracy:
- Clot activator tubes: Process within 2 hours of collection
- EDTA tubes: Stable 24 hours refrigerated
- Citrate tubes: Process within 4 hours (preferably 1 hour)
- Heparin tubes: Process within 1 hour for optimal results
Emerging Trends in Blood Collection Technology
Innovation continues advancing blood collection tube design and functionality. Recent developments include:
Gel-free separators: Mechanical barriers eliminating gel interference in mass spectrometry applications
Reduced-volume pediatric tubes: 0.5-1ml capacity micro-collection systems minimizing blood loss in neonatal and pediatric populations
Stabilization additives: Extended room-temperature stability formulations enabling 48-72 hour ambient storage for specific analytes
Sustainable materials: Bio-based plastic alternatives reducing environmental impact while maintaining performance specifications


Conclusion: Strategic Selection of Blood Collection Tubes
The selection of appropriate blood collection tubes represents a critical decision impacting diagnostic accuracy, operational efficiency, and cost management. Understanding the types of blood collection tubes, their specific applications in blood collection tubes and tests protocols, and the considerations guiding selection among different tubes for blood collection enables healthcare facilities to optimize laboratory operations.
For facilities seeking reliable supply partnerships, direct factory sourcing of vacuum blood collection tubes—particularly versatile 5ml clot activator tubes—offers quality assurance, competitive pricing, and supply chain stability. The combination of PET material construction, comprehensive size ranges (12×75 through 16×100), appropriate certifications (CE/ISO), and proper shelf life management creates a foundation for consistent, high-quality diagnostic testing.
Whether managing a high-volume hospital laboratory processing thousands of specimens daily or a smaller clinic with focused testing needs, strategic tube selection supported by knowledgeable suppliers ensures that diagnostic excellence begins at the moment of collection—where precision, quality, and reliability matter most.