In today’s healthcare landscape, few medical devices are as essential and widely used as the disposable hypodermic syringe. Whether it’s administering routine vaccines or delivering life-saving medications, these seemingly simple instruments are fundamental to patient care across the globe. Medical syringe sterility standards represent the backbone of safe injection practices, ensuring every procedure meets the highest safety requirements. Yet behind their straightforward design lies a sophisticated network of manufacturing precision, rigorous quality control, and—most critically—sterility protocols that can literally make the difference between life and death. Understanding medical syringe sterility standards is crucial for healthcare providers, manufacturers, and patients alike.
The Cornerstone of Safe Medical Practice
When it comes to medical devices, sterility standards aren’t just recommended—they’re absolutely non-negotiable. Consider this: hypodermic syringes directly penetrate the body’s first line of defense—our skin. This makes maintaining complete sterility not just important, but essential. Every single syringe must be manufactured, packaged, and stored under conditions that completely eliminate any chance of microbial contamination.
True sterility goes way beyond being simply “clean.” A genuinely sterile syringe is totally free from all forms of microbial life—we’re talking bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores. Achieving this level of cleanliness requires stringent manufacturing processes and proven sterilization methods that have been perfected through decades of medical innovation.
What Happens When Sterility Breaks Down
Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) rank among the most serious threats in modern medicine. When contaminated syringes make it into clinical use, patients face immediate and potentially devastating risks:
Bacterial Infections: Contaminated syringes can pump dangerous bacteria straight into the bloodstream or surrounding tissues, potentially triggering sepsis, painful abscesses, or stubborn localized infections requiring aggressive antibiotic therapy.
Viral Transmission: This is where things get really scary. Contaminated injection equipment can spread bloodborne pathogens like Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, and HIV—infections that can change lives forever.
Fungal Complications: While less common, fungal infections from dirty syringes are notoriously difficult to treat and can lead to serious system-wide infections, particularly dangerous for patients with compromised immune systems.
Endotoxin Reactions: Even when live bugs aren’t present, bacterial toxins can still cause severe inflammatory responses, high fevers, and in worst-case scenarios, life-threatening endotoxic shock.
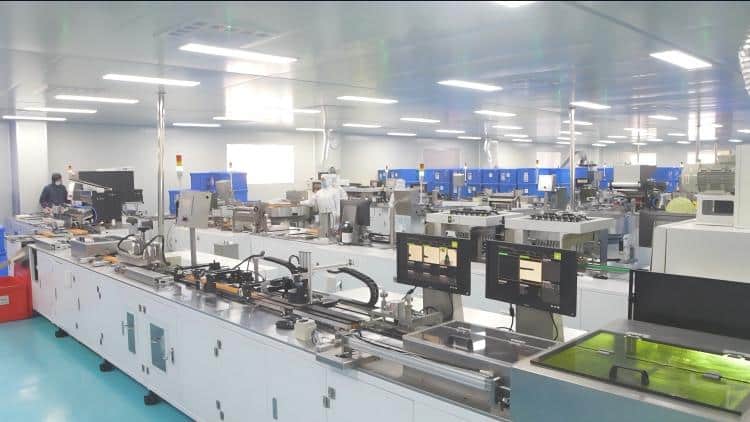

From Raw Materials to Sterile Product: The Manufacturing Journey
Creating a sterile disposable syringe involves multiple critical checkpoints, each designed to establish and verify sterility:
Material Selection and Testing: Everything starts with carefully chosen medical-grade plastics that undergo extensive testing for biocompatibility and sterility. These materials must meet strict regulatory standards and demonstrate consistent performance characteristics.
Cleanroom Manufacturing: Production happens in highly controlled cleanroom environments featuring advanced air filtration, precise temperature control, and regulated humidity. Workers follow strict protocols—specialized clothing, rigorous hand hygiene, and restricted access—all to maintain that sterile environment.
Automated Assembly: Today’s syringe manufacturing relies heavily on automated systems that minimize human contact with the product. These systems undergo regular validation and monitoring to ensure sterile conditions are maintained throughout the entire assembly process.
Sterilization Methods: Most disposable syringes are sterilized using one of several proven methods:
- Gamma radiation sterilization—penetrates right through packaging to eliminate microorganisms
- Ethylene oxide (EtO) gas sterilization—particularly effective for heat-sensitive materials
- Electron beam sterilization—offers rapid processing with minimal heat generation
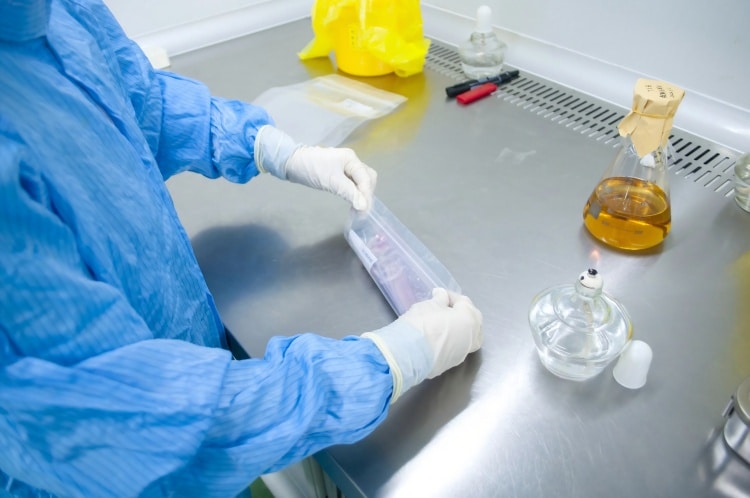

Quality Assurance: Testing That Goes the Distance
Ensuring sterility demands comprehensive testing protocols that go far beyond a simple visual check:
Sterility Testing: Samples from every production batch undergo rigorous sterility testing following pharmacopeial standards. These tests involve incubating samples in growth media to detect any viable microorganisms.
Bioburden Testing: Before sterilization, products are tested for their microbial load to ensure sterilization parameters will be appropriate and effective.
Sterility Assurance Level (SAL): The industry gold standard requires achieving a SAL of 10^-6—meaning there’s less than one chance in a million that any viable microorganism survives the sterilization process.
Environmental Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of the manufacturing environment ensures conditions stay within acceptable parameters throughout the entire production run.
Packaging: The Final Line of Defense
Sterile packaging serves as the ultimate protection for syringes right up until the moment they’re used. This packaging must:
Maintain Sterility: Provide an effective barrier against microbial contamination while still allowing sterilization agents to penetrate during processing.
Enable Aseptic Opening: Allow healthcare providers to access the syringe without compromising sterility through specially designed opening mechanisms.
Include Sterility Indicators: Feature chemical or biological indicators that provide visual confirmation of successful sterilization.
Ensure Long-Term Stability: Maintain sterility throughout the product’s intended shelf life—typically several years when stored correctly.
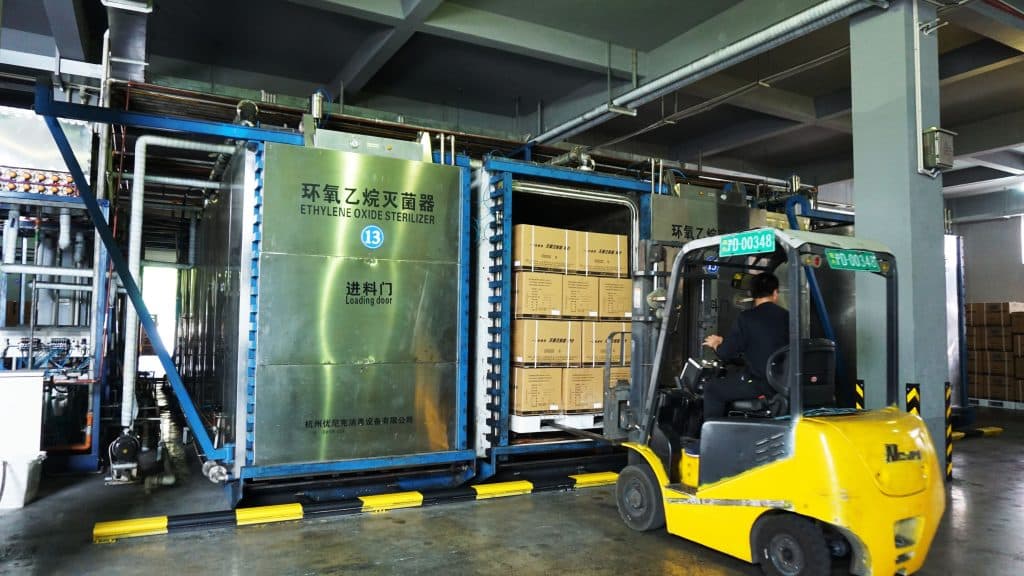

Global Standards and Regulatory Oversight
The critical importance of syringe sterility is recognized worldwide through comprehensive regulatory frameworks:
International Standards: ISO 13485 and ISO 11607 provide globally recognized standards for medical device quality management and sterile packaging.
Regulatory Bodies: Organizations like the FDA here in the US, the European Medicines Agency in Europe, and China’s National Medical Products Administration maintain strict oversight of syringe manufacturing and sterility requirements.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP): These guidelines ensure manufacturing processes consistently produce products that meet predetermined quality specifications.
The Bottom Line: Economic Impact of Sterility
While maintaining sterility requires serious investment in facilities, equipment, and processes, the economic benefits far outweigh the costs:
Preventing Healthcare-Associated Infections: Every infection prevented saves healthcare systems thousands of dollars in additional treatment costs, extended hospital stays, and potential legal liability.
Fighting Antibiotic Resistance: By preventing infections at their source, sterile injection practices help combat the growing threat of antibiotic-resistant organisms.
Building Patient Trust: Reliable sterility standards build public confidence in healthcare systems and vaccination programs.
Cutting-Edge Innovations in Sterility Assurance
The field of sterility assurance continues to evolve with breakthrough technologies:
Advanced Packaging Materials: Next-generation barrier materials offer enhanced protection while reducing environmental impact.
Real-Time Monitoring: Sensor technologies now enable continuous monitoring of sterility parameters throughout manufacturing and storage.
Automated Quality Control: AI and machine learning are being integrated into quality control processes to improve detection of potential sterility breaches.
Sustainable Sterilization Methods: Research into environmentally friendly sterilization alternatives continues to advance while maintaining gold-standard efficacy.
Best Practices for Healthcare Providers
Even with perfectly sterile syringes, healthcare providers play a crucial role in maintaining that sterility:
Proper Storage: Syringes must be stored in clean, dry environments away from potential contamination sources.
Aseptic Technique: Healthcare workers must follow established protocols for opening sterile packages and handling syringes.
Single-Use Compliance: Disposable syringes must never, ever be reused—regardless of how clean they might appear or any sterilization attempts.
Ongoing Training: Regular education ensures all healthcare personnel understand and consistently follow sterility protocols.
Looking Ahead
As healthcare continues to evolve, the importance of sterility in disposable syringes will only continue to grow. Emerging challenges like new infectious diseases, increasingly complex patient needs, and global health initiatives all underscore the critical need for reliable, sterile injection equipment.
The development of smart syringes with built-in safety features, biodegradable materials that maintain sterility standards, and enhanced tracking systems for supply chain integrity represent just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to future innovations.

The Bottom Line
The sterility of disposable hypodermic syringes represents one of the most fundamental aspects of patient safety in modern healthcare. From the moment raw materials enter the manufacturing facility to the point where the needle enters a patient’s skin, every single step in the process is designed to ensure patients receive the safest possible care.
As we continue to face global health challenges, maintaining the highest medical syringe sterility standards isn’t just important—it’s absolutely critical. The investment in sterility assurance isn’t simply a regulatory checkbox or manufacturing consideration—it’s a sacred commitment to patient safety that forms the bedrock of trust between healthcare providers and the patients they serve.
Through continued innovation, uncompromising quality control, and unwavering dedication to safety standards, the medical device industry ensures that every injection delivered through a disposable syringe meets the gold standard of sterility and safety. In healthcare, there’s simply no room for compromise when it comes to putting safety first.
This commitment to sterility extends far beyond individual patient encounters to encompass public health initiatives, emergency response scenarios, and global vaccination programs. As we look toward the future of healthcare delivery, the principles of sterile injection practices will continue to serve as the fundamental pillars of safe, effective medical care worldwide.