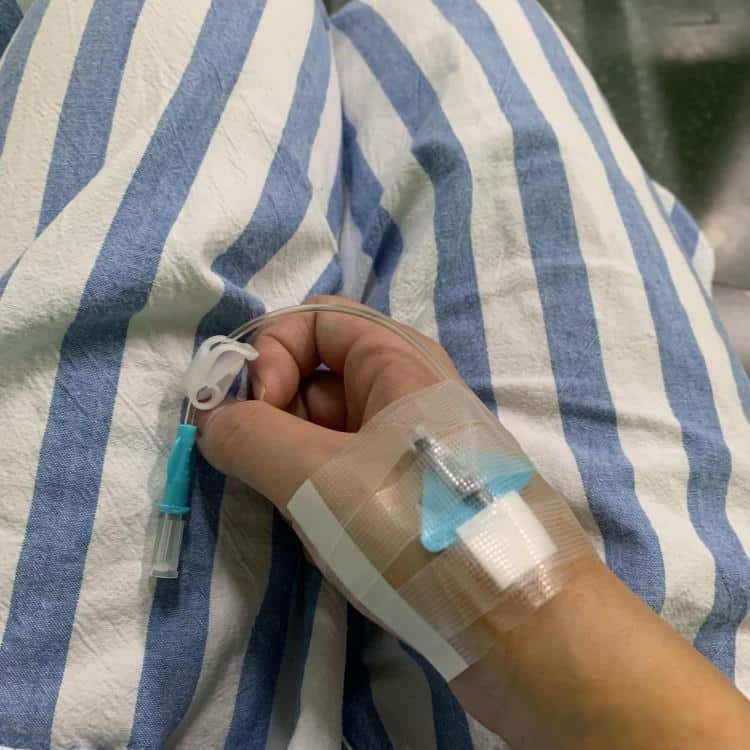
What is a Peripheral IV Catheter?
A peripheral IV catheter (also known as peripheral intravenous catheter, IV cannula, or PIVC) is a flexible tube inserted into a peripheral vein to provide vascular access for medication administration, fluid therapy, and blood sampling. These medical catheters consist of several key components:
- Catheter hub: Color-coded connector that attaches to IV tubing
- Catheter shaft: Flexible tube made from biocompatible materials (typically polyurethane or Teflon)
- Introducer needle: Sharp needle that facilitates initial vein puncture
- Safety mechanism: Prevents accidental needlestick injuries
- Flashback chamber: Confirms successful venous access through blood return
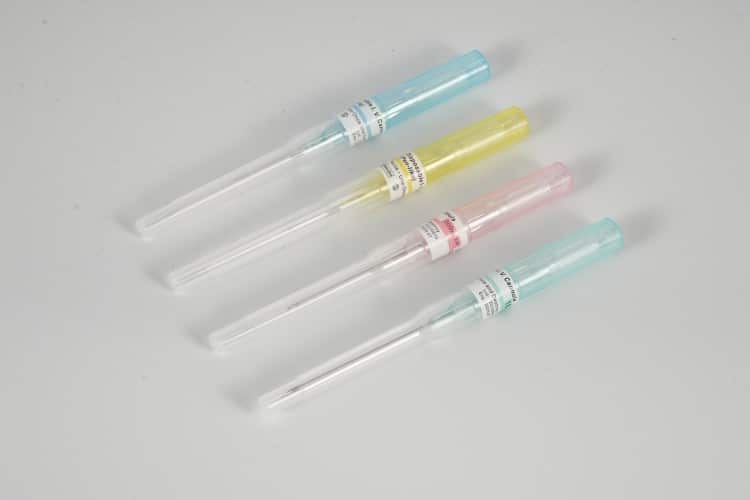
IV catheters are classified by gauge size, with smaller numbers indicating larger diameters. Common sizes include 14G IV catheter, 16G IV catheter, 18G IV catheter, 20G IV catheter, 22G IV catheter, and 24G IV catheter. The choice of catheter gauge depends on patient factors, infusion requirements, and clinical indication.
Abstract
Peripheral IV catheter insertion represents one of the most frequently performed procedures in modern healthcare, with over 3 billion IV cannulas used annually across North America and Europe. This comprehensive guide examines evidence-based IV insertion techniques, advanced catheter technologies, and quality improvement strategies based on FDA guidelines, INS standards, and European Vascular Access Society recommendations.
1. Vascular Anatomy and Physiological Foundations
1.1 Venous Structure and IV Catheter Compatibility
Vessel Wall Architecture:
- Tunica intima: 0.1-0.2mm thickness; critical for catheter biocompatibility
- Tunica media: 0.1-0.5mm in veins; determines vessel elasticity for IV catheter placement
- Tunica adventitia: Provides 60-70% of vessel strength; affects catheter securement
Optimal Catheter-to-Vein Ratio: The vessel diameter should be ≥3 times the outer diameter of IV catheter for optimal flow and reduced complications:
- 24G peripheral IV catheter (0.7mm): Requires ≥2.1mm vessel
- 22G IV cannula (0.9mm): Requires ≥2.7mm vessel
- 20G IV catheter (1.1mm): Requires ≥3.3mm vessel
- 18G peripheral catheter (1.3mm): Requires ≥3.9mm vessel
1.2 Age-Related Vascular Changes
Pediatric Considerations (0-12 years):
- Vessel diameter: 30-60% of adult size
- Pediatric IV catheters (24G) recommended
- Success rates: 85-95% with experienced operators
Geriatric Modifications (≥65 years):
- Vessel fragility increases IV catheter insertion difficulty
- Success rates decrease to 65-75%
- Safety IV catheters with smaller gauges preferred
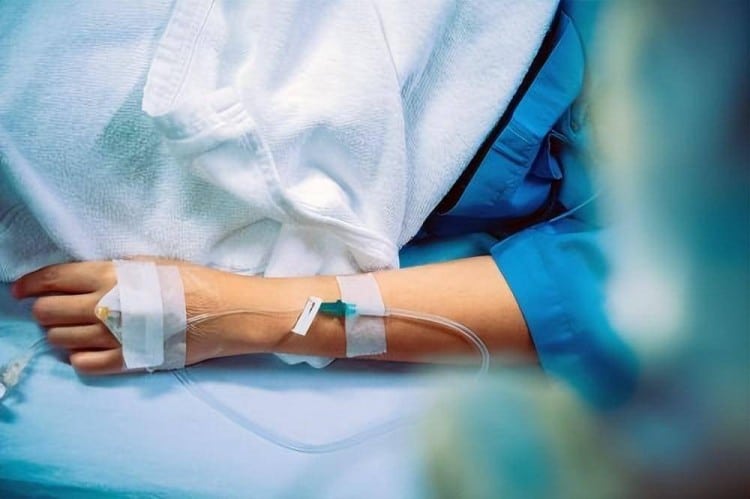
2. Advanced Catheter Technologies
2.1 Material Science in IV Catheter Manufacturing
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) IV Catheters:
- Superior biocompatibility with 18.5 mN/m surface tension
- Thrombosis rate <2% within 72 hours
- Enhanced chemical resistance for diverse medications
Polyurethane (PU) Peripheral Catheters:
- Tensile strength: 45-65 MPa
- Catheter softening technology reduces vessel trauma
- Biodegradation rate <0.5% annually
Catheter Flow Rate Optimization:
| IV Catheter Size | Internal Diameter | Flow Rate (mL/min) | Clinical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| 24G IV catheter | 0.56mm | 13-17 | Pediatrics, fragile veins |
| 22G peripheral IV | 0.72mm | 25-35 | Standard adult therapy |
| 20G IV cannula | 0.88mm | 55-65 | Rapid fluid resuscitation |
| 18G IV catheter | 1.07mm | 90-110 | Blood transfusion, surgery |
2.2 Safety IV Catheter Innovations
Needlestick Prevention Technology:
- Safety IV catheters reduce injury risk by 85%
- Automatic needle retraction mechanisms
- OSHA compliance for bloodborne pathogen protection
Antimicrobial IV Catheters:
- Silver-ion coating technology
- Catheter-related infection rates reduced by 40-60%
- Extended dwell time up to 120 hours
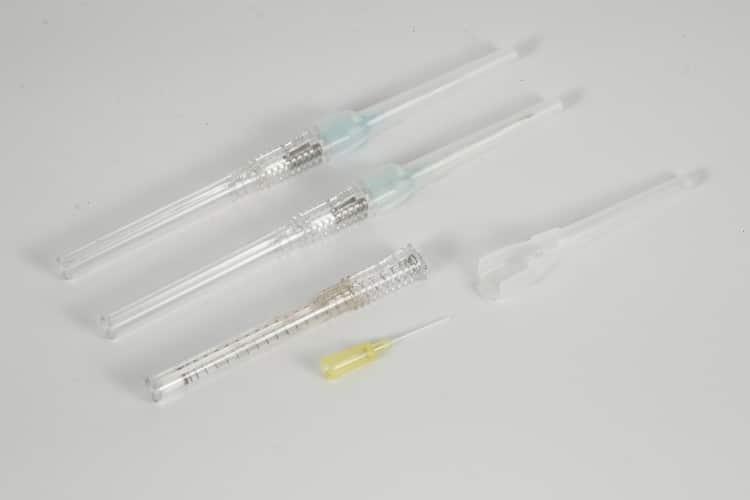
3. Evidence-Based Insertion Techniques
3.1 Pre-Insertion Assessment Protocol
Vascular Assessment Criteria:
- Ultrasound-guided IV insertion for difficult access patients
- Vessel compressibility >30% indicates good elasticity
- IV catheter placement site selection avoiding joints and valves
Patient Risk Stratification:
- Coagulation parameters: PLT >100×10⁹/L, PT <1.5× normal
- Difficult IV access factors: BMI >30, previous failed attempts
- Peripheral IV therapy contraindications assessment
3.2 Ultrasound-Guided IV Catheter Insertion
Technical Specifications:
- Ultrasound frequency: 10-15MHz for optimal vessel imaging
- Success rate improvement: 85-95% vs 40-60% traditional method
- Cost-effectiveness: ROI achieved within 3.4 months
Procedural Steps:
- Dynamic needle visualization during catheter insertion
- Real-time catheter advancement confirmation
- Saline flush verification through color Doppler
3.3 Insertion Angle and Technique Optimization
Critical Technical Parameters:
- Insertion angle: 15-30° for optimal catheter threading
- Needle advancement speed: 2-3mm/second
- Catheter hub stabilization during needle withdrawal

4. Complication Prevention and Management
4.1 Catheter-Related Thrombosis Prevention
Pathophysiology of IV Catheter Thrombosis:
- Virchow’s triad: endothelial damage, blood stasis, hypercoagulability
- Catheter material biocompatibility reduces thrombogenic risk
- Proper catheter size selection minimizes vessel trauma
Prevention Strategies:
- Saline flush protocols: 5-10mL before and after medication administration
- Catheter securement devices prevent mechanical trauma
- IV catheter dwell time monitoring (recommended <96 hours)
4.2 Infection Control for IV Catheters
Microbiology of Catheter-Related Infections:
- Staphylococcus epidermidis: Most common pathogen (45%)
- Candida species: Increasing incidence in immunocompromised patients
- MRSA colonization: 15-30% prevalence in healthcare settings
Evidence-Based Prevention:
- 2% chlorhexidine skin preparation: 99.9% bacterial reduction
- Sterile technique for IV catheter insertion
- Catheter site dressing changes every 7 days or when compromised
4.3 Phlebitis Risk Reduction
Phlebitis Scale Assessment:
- Grade 0: No symptoms
- Grade 1: Erythema at access site
- Grade 2: Pain, erythema, and/or edema
- Grade 3: Streak formation, palpable venous cord
- Grade 4: Purulent drainage
Risk Mitigation:
- pH-neutral IV solutions reduce chemical irritation
- Catheter rotation every 72-96 hours
- Peripheral IV site assessment every 4-8 hours
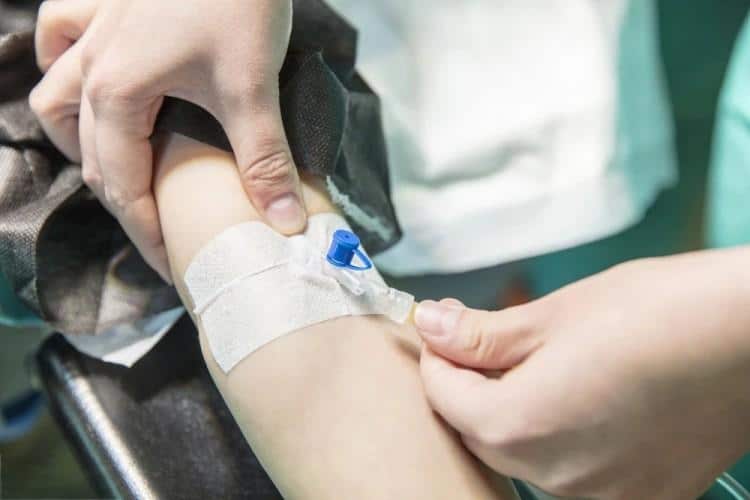
5. Quality Management and Performance Metrics
5.1 Six Sigma Methodology in IV Catheter Programs
Key Performance Indicators:
- First-attempt success rate: Target ≥90%
- IV catheter complications: <3% incidence
- Patient satisfaction scores: ≥95% for catheter insertion experience
- Cost per successful catheter: $180-300 reduction with quality improvement
Statistical Process Control:
- Control charts for insertion success rates
- Pareto analysis of failure modes
- Root cause analysis for catheter-related adverse events
5.2 Economic Impact of IV Catheter Quality
Cost-Benefit Analysis:
- Failed IV insertion cost: $180-300 per occurrence
- Annual savings potential: $50,000-$80,000 (1000-bed hospital)
- Ultrasound-guided insertion ROI: 1:3.5-4.2 within first year
6. Future Innovations in IV Catheter Technology
6.1 Smart Catheter Systems
Integrated Sensor Technology:
- Pressure-sensing IV catheters with MEMS technology
- Real-time patency monitoring through wireless transmission
- Predictive algorithms for catheter failure prevention
6.2 Robotic-Assisted IV Insertion
Technical Capabilities:
- Positioning accuracy: ±0.5mm precision
- Success rates: >95% in preliminary trials
- Standardized insertion parameters reduce operator variability
6.3 Personalized Medicine Applications
Pharmacogenomic Considerations:
- CYP2C19 genotyping for antiplatelet therapy
- Factor V Leiden testing for thrombosis risk
- Individualized catheter selection based on genetic markers

7. Manufacturer Excellence and Innovation
7.1 Our Advanced IV Catheter Technology
Material Innovation:
- Third-generation biocompatible polymers for enhanced catheter performance
- Nano-silver antimicrobial coating reduces infection risk by 60%
- Hydrophilic surface modification decreases insertion force by 40%
Manufacturing Excellence:
- Laser precision cutting for optimal needle sharpness
- Six-axis CNC machining ensures dimensional accuracy
- ISO 13485 certified automated sterile packaging lines
- FDA 21 CFR Part 820 compliant quality systems
Clinical Performance Advantages:
- Insertion resistance reduction: 40% compared to standard catheters
- Extended dwell time: Up to 120 hours with minimal complications
- Blood compatibility improvement: 60% better hemocompatibility
- Catheter-related infection rate: Reduced to <0.3‰
7.2 Global Technical Support Network
Comprehensive Service Portfolio:
- 24/7 technical hotline for IV catheter troubleshooting
- On-site training programs for optimal catheter insertion techniques
- Customized solutions for specific clinical requirements
- Continuous product improvement based on clinical feedback
Quality Assurance Commitment:
- Complete regulatory compliance: FDA, CE Mark, ISO certifications
- Global product liability coverage for peace of mind
- Five-year quality guarantee on all IV catheter products
- 48-hour response time for adverse event investigations
Research and Development Investment:
- 15% annual revenue allocation to R&D initiatives
- Clinical partnerships with 10+ leading medical centers
- 30+ core technology patents in IV catheter innovation
- Continuous evidence generation through clinical studies
7.3 Why Choose Our IV Catheters
Our peripheral IV catheters represent the pinnacle of medical device engineering, combining advanced materials science with precision manufacturing. We understand that every IV insertion impacts patient care quality, driving our commitment to continuous innovation and excellence.
Key Differentiators:
- ✅ Superior catheter biocompatibility with proven clinical outcomes
- ✅ Reduced insertion complications through advanced design
- ✅ Extended catheter performance with longer dwell times
- ✅ Comprehensive technical support from design to implementation
- ✅ Regulatory compliance excellence across global markets
Conclusion
Peripheral IV catheter insertion remains a cornerstone of modern medical practice, requiring expertise in vascular anatomy, catheter technology, and evidence-based techniques. As healthcare continues evolving toward precision medicine and improved patient outcomes, the selection of high-quality IV catheters becomes increasingly critical.
Our commitment to catheter innovation and manufacturing excellence ensures healthcare professionals have access to the most advanced peripheral IV catheter technology available. Through continuous research, quality improvement, and clinical collaboration, we support the global medical community in delivering safe, effective vascular access care.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications:
- FDA 21 CFR Part 820 Quality System Regulation
- ISO 10555 Medical Catheters Standards
- USP Class VI Biocompatibility Testing
- AAMI/ANSI/ISO 11137 Sterilization Standards