Introduction
Insulin pen needles serve as critical tools for daily insulin injection in diabetes patients, with their proper selection and use directly impacting treatment efficacy and patient safety. According to International Diabetes Federation (IDF) data, approximately 537 million adults worldwide have diabetes, with a significant proportion requiring insulin therapy. This article provides a technical perspective on the selection criteria and standardized usage protocols for insulin safety pen needles.
I. Technical Specifications and Classification of Insulin Pen Needles
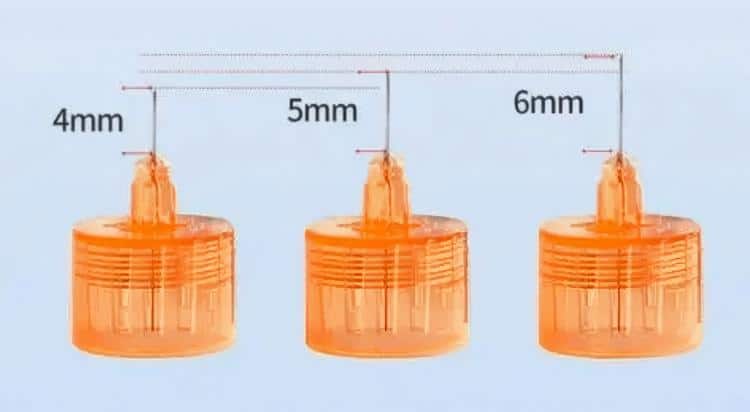
1.1 Needle Length Classification
Insulin pen needles are categorized by length as follows:
- Ultra-short needles (4mm): Suitable for children and lean adults
- Short needles (5-6mm): Suitable for most adult patients
- Standard needles (8mm): Suitable for obese patients or those with thicker subcutaneous fat
- Long needles (12.7mm): Currently rarely used, mainly for special circumstances
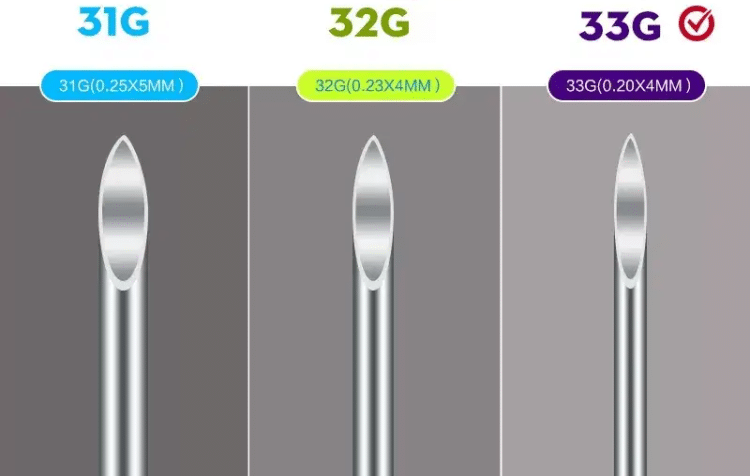
1.2 Needle Gauge Specifications (Needle Diameter)
Classification by needle diameter:
- 32G (0.23mm): Finest specification, lowest pain sensation
- 31G (0.25mm): Fine needle, balances comfort and flow rate
- 30G (0.30mm): Standard specification, broad applicability
- 29G (0.33mm): Larger diameter, minimal injection resistance
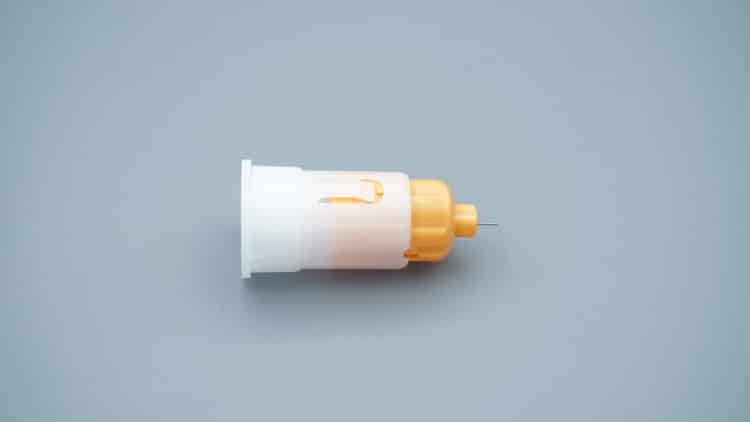
1.3 Safety Design Features
Modern insulin pen needles universally incorporate the following safety technologies:
- Triple-bevel design: Reduces tissue trauma, decreases pain
- Silicone coating: Reduces injection resistance, enhances comfort
- Safety cap design: Prevents accidental needle sticks
- Single-use only: Eliminates cross-contamination risk
II. Scientific Basis for Pen Needle Selection
2.1 Body Type-Based Selection Criteria
Pediatric Patients (<18 years):
- Recommend 4-5mm short needles
- Prefer 32G fine gauge
- BMI <18.5 mandates 4mm needle use
Adult Patient Selection Matrix:
| BMI Range | Recommended Length | Alternative Length | Gauge Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| <18.5 | 4mm | 5mm | 32G |
| 18.5-24.9 | 5-6mm | 4mm/8mm | 31-32G |
| 25-29.9 | 6-8mm | 5mm | 30-31G |
| ≥30 | 8mm | 6mm | 29-30G |
2.2 Injection Site Considerations
Abdominal Injection:
- Subcutaneous fat thickness: 8-15mm
- Recommended length: 4-6mm
- Injection angle: 90° perpendicular
Outer Thigh:
- Subcutaneous fat thickness: 10-20mm
- Recommended length: 5-8mm
- Injection angle: 90° or 45°
Outer Upper Arm:
- Subcutaneous fat thickness: 6-12mm
- Recommended length: 4-6mm
- Avoid muscle layer penetration
III. Proper Usage Steps for Insulin Pen Needles
3.1 Pre-Use Preparation (2-3 minutes)
Step 1: Environmental Setup
- Select clean, well-lit environment
- Prepare alcohol swabs or disinfectant wipes
- Check insulin pen and needle packaging integrity
Step 2: Hand Hygiene
- Wash hands with soap and warm water for 15-20 seconds
- Or use 75% alcohol-based hand sanitizer
Step 3: Equipment Inspection
- Check insulin expiration date and appearance
- Confirm needle packaging is undamaged
- Verify insulin type matches prescription
3.2 Needle Installation Process (30-60 seconds)
Step 1: Remove Insulin Pen Cap
- Rotate clockwise to remove pen cap
- Check pen head threading integrity
Step 2: Install Pen Needle
- Tear open needle outer packaging
- Align needle straight with pen head threading
- Rotate clockwise until secure (avoid over-tightening)
Step 3: Remove Needle Protective Caps
- First remove outer protective cap and retain
- Then remove inner protective cap and discard
3.3 Insulin Preparation (1-2 minutes)
Step 1: Air Test
- Set dose to 2 units
- Point needle up, pen body down
- Press injection button until insulin droplet appears
Step 2: Dose Setting
- Set accurate dose according to medical orders
- Confirm dose window displays correct value
- Check sufficient insulin remains
3.4 Skin Preparation and Injection (2-3 minutes)
Step 1: Injection Site Selection
- Minimum 2.5cm distance from previous injection
- Avoid scars, indurations, or inflamed areas
- Follow rotation principle for injection areas
Step 2: Skin Disinfection
- Wipe with alcohol swab in spiral pattern
- Disinfection area diameter: 5cm
- Wait for alcohol to evaporate naturally (15-30 seconds)
Step 3: Injection Procedure
- Insert at 90° perpendicular (4-6mm needles)
- Or insert at 45° angle (8mm+ needles)
- Slowly depress injection button to bottom
- Maintain pressure for 10 seconds
3.5 Post-Injection Handling (1-2 minutes)
Step 1: Needle Removal
- Withdraw needle vertically and quickly
- Avoid needle movement within skin
- Lightly press injection site with clean cotton ball
Step 2: Needle Disposal
- Replace outer protective cap
- Rotate counterclockwise to remove needle
- Place used needle in dedicated sharps container

IV. Safety Precautions and Risk Control
4.1 Infection Control Measures
Single-Use Principle:
- Each needle used only once
- Discard immediately after use
- Prohibit reuse or sharing with others
Disinfection Standards:
- Pre-injection skin disinfection: 100% coverage
- Alcohol concentration requirement: 75%
- Post-disinfection wait time: ≥15 seconds
4.2 Needlestick Injury Prevention
Operational Safety Requirements:
- Keep needle pointing down during installation/removal
- Avoid fingers near needle tip during two-handed operations
- Immediately recap after injection completion
Accident Response Protocol:
- Immediately flush wound with soap and water
- Express small amount of blood
- Disinfect with iodine solution
- Document incident and seek medical advice
4.3 Storage and Waste Disposal
Needle Storage Requirements:
- Store at room temperature (15-30°C)
- Avoid direct sunlight and high temperatures
- Keep packaging sealed until use
Medical Waste Disposal:
- Use dedicated sharps disposal containers
- Seal container when 2/3 full
- Follow medical waste disposal regulations for processing
V. Common Issues and Solutions
5.1 Injection Pain Control
Pain Cause Analysis:
- Needle too thick (>30G)
- Injection speed too rapid
- Needle reuse causing dulling
- Improper injection angle
Improvement Measures:
- Select 32G ultra-fine needles
- Control injection speed (1 unit/second)
- Strict single-use compliance
- Ensure 90° perpendicular insertion
5.2 Insulin Leakage Management
Leakage Causes:
- Premature needle withdrawal (<10 seconds)
- Improper needle insertion angle
- Insufficient subcutaneous fat layer
Prevention Measures:
- Maintain 10-second hold after injection completion
- Ensure complete subcutaneous penetration
- Select appropriate length based on body type
5.3 Lipodystrophy Prevention
High-Risk Factors:
- Repeated injection at same site
- Needle reuse
- Improper injection technique
Prevention Strategies:
- Establish injection rotation schedule
- ≥2.5cm injection spacing
- Regular injection site inspection

VI. Quality Monitoring and Effectiveness Assessment
6.1 Blood Glucose Monitoring Indicators
Monitoring Frequency:
- Pre-meal glucose: 3 times daily
- 2-hour post-meal glucose: 3 times daily
- HbA1c: Every 3 months
Target Ranges:
- Fasting glucose: 4.4-7.0 mmol/L
- Post-meal glucose: <10.0 mmol/L
- HbA1c: <7.0%
6.2 Injection Site Assessment
Assessment Frequency: Weekly comprehensive examination
Assessment Components:
- Skin integrity
- Lipodystrophy formation
- Infection signs
- Fat atrophy or hypertrophy

Conclusion
Proper selection and use of insulin safety pen needles represents a critical component in ensuring treatment effectiveness for diabetes patients. Through adherence to scientific selection criteria, standardized operational procedures, and strict safety measures, injection safety and comfort can be significantly enhanced while optimizing glycemic control outcomes. Patients should master proper injection techniques under healthcare professional guidance, regularly assess injection effectiveness, and promptly adjust injection protocols to achieve optimal therapeutic goals.
Regular technical training and operational assessment serve as important safeguards for ensuring injection quality. It is recommended that patients receive professional injection technique evaluation and guidance every 6 months to ensure continued treatment effectiveness and safety.